Overview
This page presents the Adaptive User Interface System Ontology (AUISO). AUISO structures knowledge about adaptive interactive systems and the user interface customizations they can perform. The content below follows the ontology specification and uses only the AUISO concepts defined in the specification.
Conceptual model (figure)
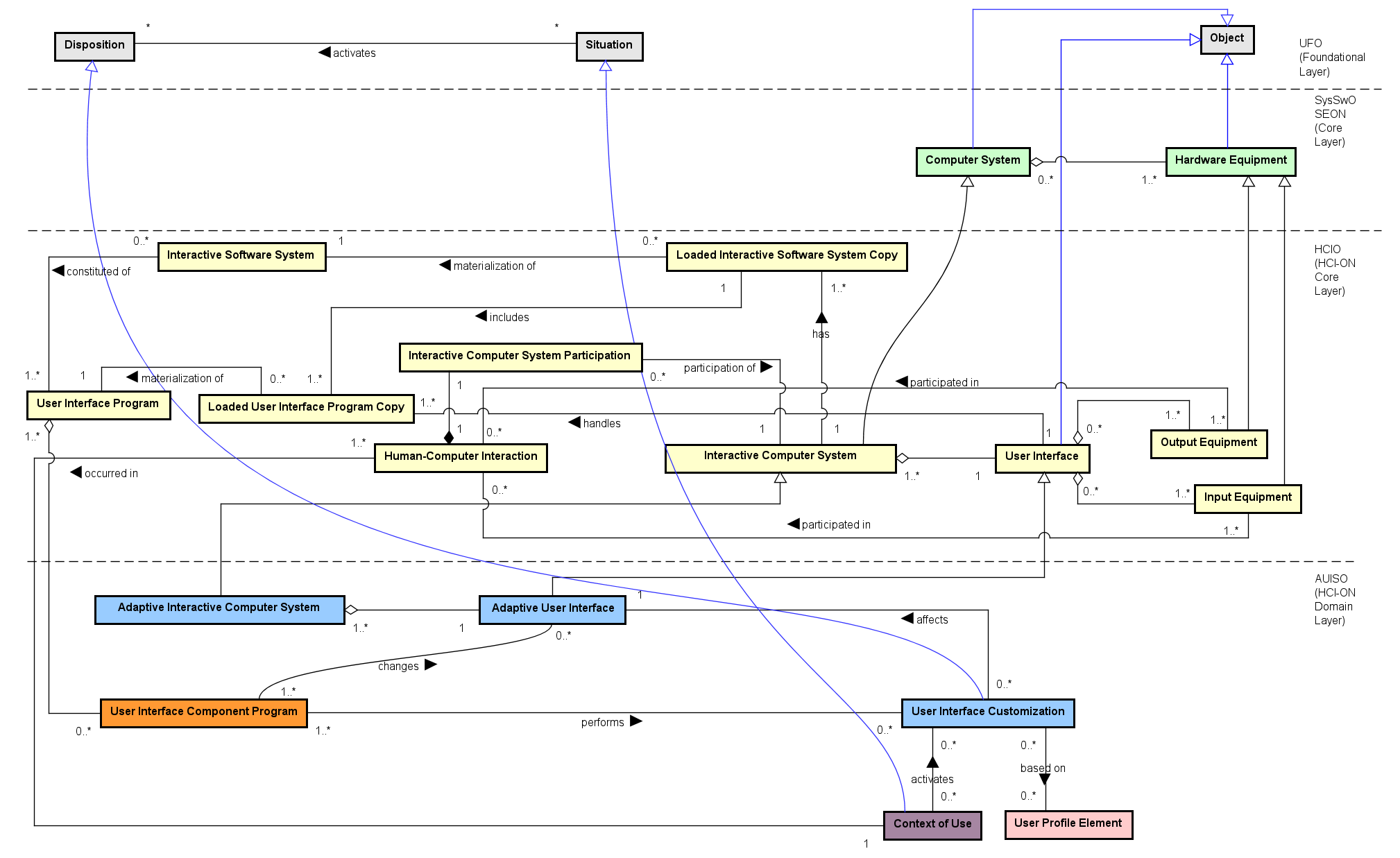 AICSAdaptive Interactive Computer System - an interactive system with adaptive UI
AUIAdaptive User Interface - a User Interface able to automatically adapt
UICUser Interface Customization - adaptation performed in the adaptive UI
UICTUser Interface Customization Type - types such as Dark Mode, Font Mode etc.
UICRUser Interface Customization Recommendation - suggestions for customizations
CoUContext of Use - situation that may activate customizations
AICSAdaptive Interactive Computer System - an interactive system with adaptive UI
AUIAdaptive User Interface - a User Interface able to automatically adapt
UICUser Interface Customization - adaptation performed in the adaptive UI
UICTUser Interface Customization Type - types such as Dark Mode, Font Mode etc.
UICRUser Interface Customization Recommendation - suggestions for customizations
CoUContext of Use - situation that may activate customizations
Figure: Adaptive User Interface System Ontology (AUISO). (Click image to enlarge - click hotspots to jump to concept)
Concepts (UFO - Foundational Layer)
- Agent Participation - Refers to the intentional involvement of an agent in an event. These are the intentional participations of agents, considered as actions. E.g.: a player's participation in a football match.
- Complex Action - A Complex Action is composed of two or more Participations. These participations can themselves be intentional (i.e., be themselves actions) or unintentional events. For @ex, the stabbing of Caesar by Brutus includes the intentional participation of Brutus and the unintentional. participation of Caesar and the knife. In a complex action, at least one participation should be intentional, i.e., an action contribution.
- Disposition - Dispositions are properties (moments) that are only manifested in particular situations and that can also fail to be manifested. When manifested, they are manifested through the occurrence of events. Take for example the disposition of a magnet m to attract metallic material. The object m has this disposition even if it is never manifested, for example, because it is never close to any magnetic material. Nonetheless, m can certainly be said to possess that intrinsic moment, which it shares with other magnets.
- Disposition Universal - It is the type of universal that categorizes individual dispositions. Fragility and Magnetism are examples of Disposition Universals. Instances of Fragility and Magnetism are particular dispositions that inhere in individual objects.
- Object - Non-agentive substantial individuals. Objects can be Physical or Social.
- Object Participation - Object Participation is a set of different ways than an object can participate in actions. There are four different types of Object Participation, namely: Creation, Termination, Change and Usage.
- Person - A human Physical Agent. E.g.: Tim Berners Lee, Dennis Ritchie, Donald Knuth.
- Situation - A situation is a particular configuration of a part of reality which can be understood as a whole. Situations can be factual or counterfactual (@e.g., the situation in which “Al Gore is the president of the USA”).
Concepts (SysSwO - Core Layer)
- Computer System - System containing one or more Computer Machines, and other Hardware Equipments connected to them, and associated software systems that are installed/loaded in these Machines (adapted from ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765:2017).
Concepts (HCIO - Core Layer)
- Human-Computer Interaction - An interaction event composed by participations of User and Interactive Computer System.
- Interactive Computer System - The computer system that participates in the interaction (may reuse SysSwO/HCIO concepts).
- Interactive Computer System Participation - The participation of an Interactive Computer System in a Human-Computer Interaction. E.g.: the participation of the mobile phone system in the human-computer interaction in which the user touches her finger to unlock her mobile phone by using her fingerprint and the mobile phone system shows a message informing that the fingerprint was not recognized; the participation of the smart watch in the human-computer interaction in which the user uses the smart watch to monitor her heart pulse.
- User - A Person who interacts with (or is expected to interact with) an Interactive Computer System.
- User Interface - All components (hardware/software) that provide information and controls for the user to accomplish tasks; Input/Output Equipment are parts of the User Interface.
- User Participation - Event in which the user participates in a Human-Computer Interaction. E.g.: user walking and unintentionally giving information about number of steps to a monitoring system loaded in her smart watch; user touching her finger to unlock her mobile phone by using her fingerprint; user interpreting a message from the mobile phone system informing that the captured fingerprint was not recognized.
Concepts (AUISO - Domain Layer)
The AUISO concepts below are described following the ontology specification. Each concept has an anchor so you can jump from the figure hotspots.
- Adaptive Interactive Computer System - an Interactive Computer System that contains an Adaptive User Interface.
- Adaptive User Interface - a User Interface able to automatically adapt itself (presentation, behavior or structure) to satisfy user needs and contextual constraints.
- User Interface Customization - an adaptation performed by an Adaptive Interactive Computer System in its Adaptive User Interface to satisfy a User. Customizations can be activated by the Context of Use and are based on UPO elements (Nominal User Profile Elements and User Profile Element Values) and on User Interface Customization Recommendations.
- User Interface Customization Type - a type/classification of customization (powertype). Examples are listed below and include modes such as Font Mode, Dark Mode, Voice Command Mode, etc.
- User Interface Customization Recommendation - a suggestion that indicates which User Interface Customization Type(s) are suitable given a User's characteristics and the Context of Use.
User Interface Customization Types (examples)
The specification lists several customization types. Below are the ones explicitly described in AUISO:
- Font Mode - adapts font size, type and spacing to improve readability and accessibility.
- Dark Mode - uses light text on dark background to reduce eye strain in low-light contexts.
- Voice Command Mode - enables voice-based interaction for hands-free control.
- Gesture Navigation Mode - enables navigation via gestures (hand/head/arm gestures).
- Readable Interface Mode - simplifies layout and text presentation for comprehension.
- Contrast Mode - increases foreground/background contrast to aid low-vision users.
- Caption Transcript Mode - shows captions/transcripts for audio/video content.
- Basic Experience Mode - simplified UI for users with low experience or cognitive/motor difficulties.
- Average Experience Mode - standard UI for typical users.
- High Experience Mode - full-featured UI for experienced users.
- Light Mode - light theme (dark text on light background).
- Mobile Mode - layout and navigation optimized for small screens.
- Desktop Mode - layout and interaction optimized for large screens/pointer devices.
- Screen Reader Mode - support for assistive technologies (TTS, keyboard navigation).
Concepts (ContUsO - Domain Layer)
- Context of Use - The Situation in which a Human-Computer Interaction occurs; it captures environmental and situational factors that influence interaction.
Concepts (UPO - Domain Layer)
- Measurable User Profile ElementType - quality-like types that allow assignment of numeric/ordered values (e.g., Age, Education Level, Experience Level).
- Nominal User Profile Element - an instance that characterizes a particular User with respect to a Nominal User Profile Element Type (e.g., Alex’s Gender = male, Alex’s Language = English).
- Nominal User Profile Element Type - qualitative types without a measurable scale (e.g., Language Type, Gender Type, Disability Type).
- User Profile Element Type - a type of intrinsic characteristic that describes aspects of a User.
- User Profile Element Value - the actual value (a quale in UFO terms) assigned to a Measurable User Profile Element Type for a specific User. Examples from the instantiation: Alex’s Age = 40, Experience Level = Basic, Education Level = Bachelor’s degree.
Instantiation example - Alex's case
The table below reproduces the AUISO instantiation extracted from Alex's scenario (Alex interacting with a social network system):
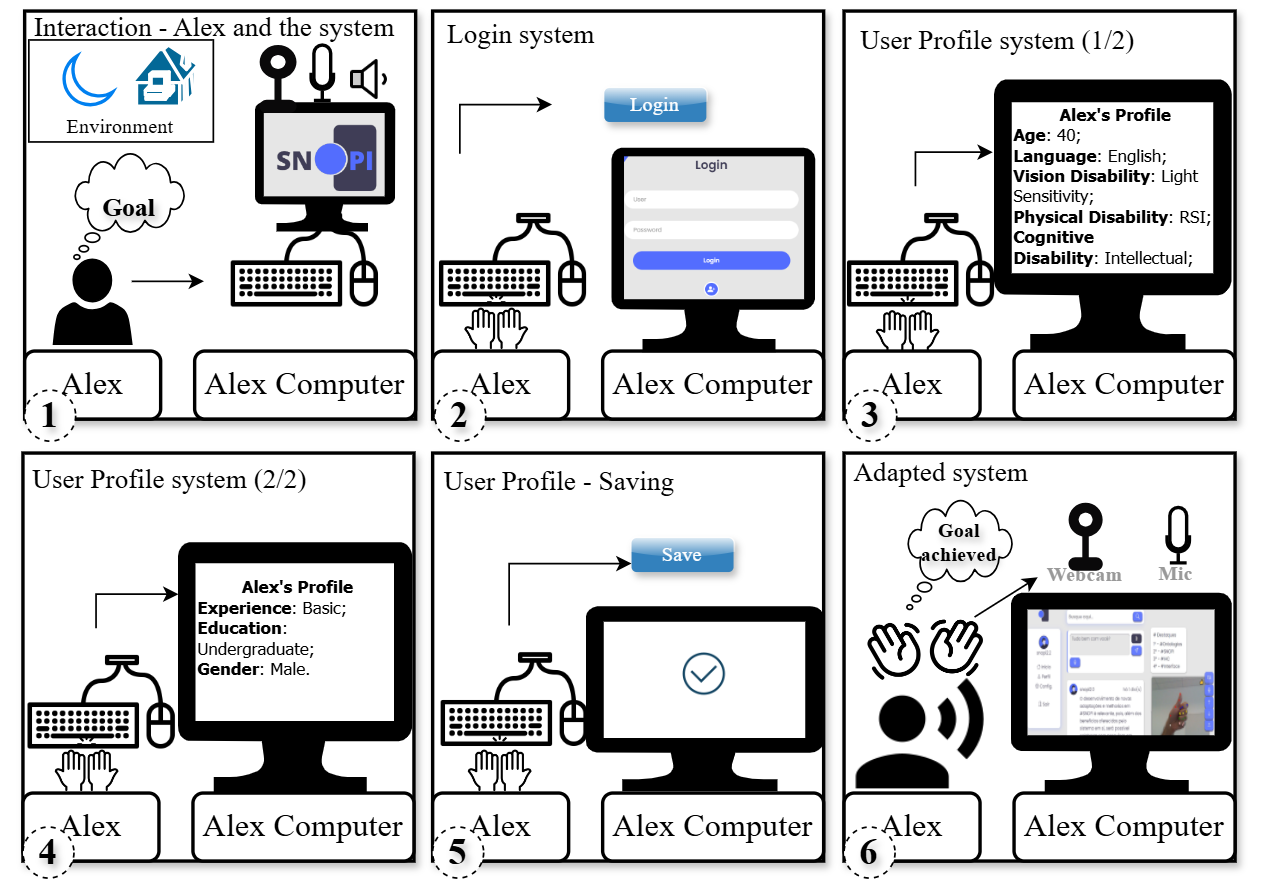
(Click to enlarge)
| Concept | Instance |
|---|---|
| Adaptive Interactive Computer System | The social network system used by Alex |
| Adaptive User Interface | The social network system's user interface |
| User Interface Customization Recommendation | Activate Dark Mode to adjust brightness and contrast if luminosity is low; activate Voice Command Mode and Gesture Navigation Mode if the user has RSI. |
| User Interface Customization Type | Dark Mode, Voice Command Mode, Gesture Navigation Mode |
| User Interface Customization | Activate Dark Mode; enable Voice Command Mode; enable Gesture Navigation Mode |
The ontologies were modeled in UML (Unified Modeling Language), but a specific representation of powertypes - when specializations of a concept are instances of another concept of a higher order - does not exist in UML. Thus, we used an adaptation (dotted arrow), following the approach for UML-based ontological modeling proposed by Guizzardi (2005), which allows for the dual nature of specializations to be adequately represented as instances of a higher-order concept within the ontology.
