Overview
This page presents the User Profile Ontology (UPO): conceptual model, figures, all main concepts with explanations, an instantiation example (Alex's case) and a short glossary.
Definitions and concept descriptions extracted from the ontology specification.
Conceptual model (figures)
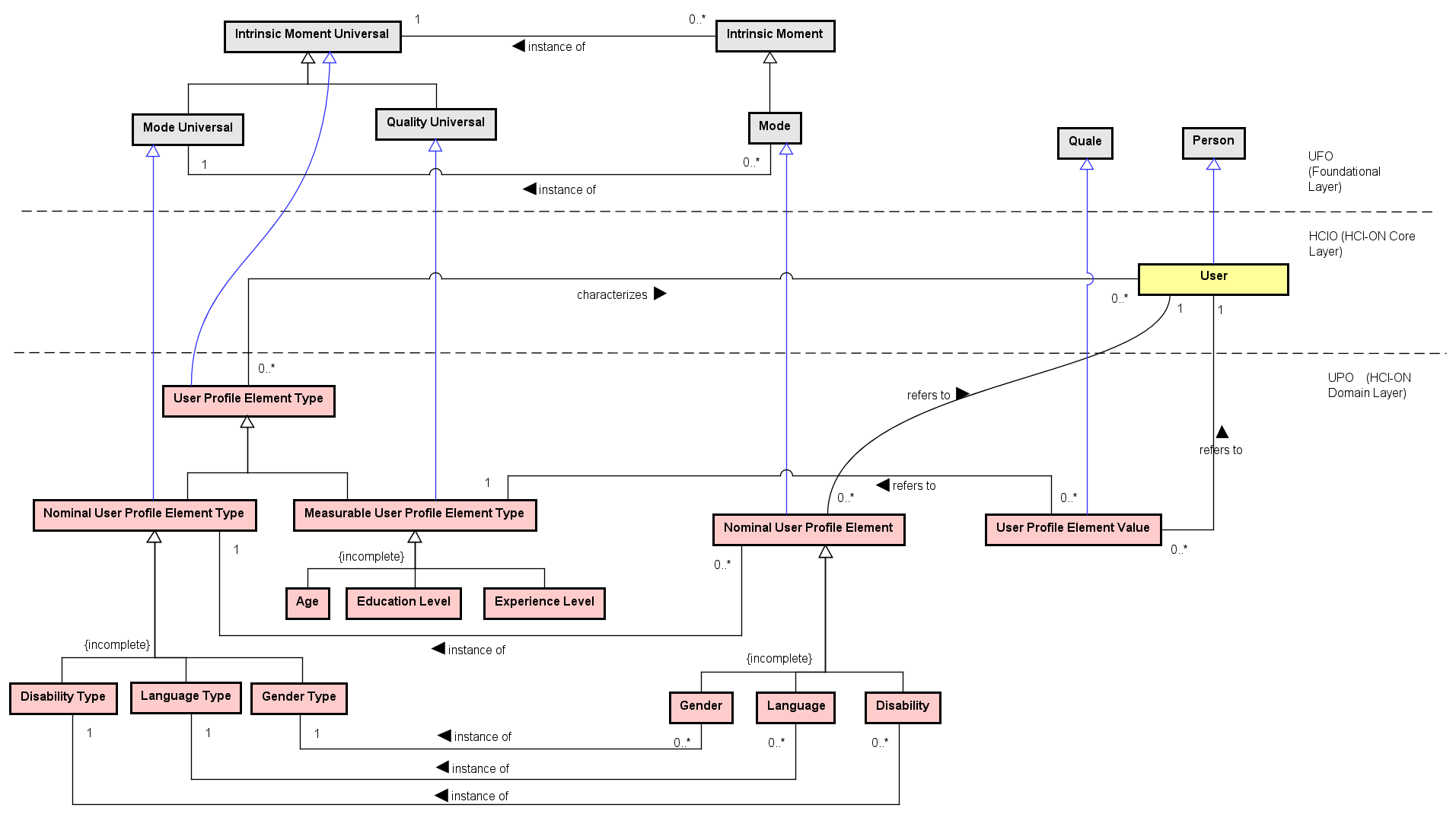 UUser - Person who interacts with the system
UPETUser Profile Element Type - types that characterize a user
MUPETMeasurable types (Age, Education, Experience)
NUPETNominal types (Gender, Language, Disability)
DDisability - different disability categories
UUser - Person who interacts with the system
UPETUser Profile Element Type - types that characterize a user
MUPETMeasurable types (Age, Education, Experience)
NUPETNominal types (Gender, Language, Disability)
DDisability - different disability categories
Figure 1: General structure of the User Profile Ontology (UPO). (Click image to enlarge - click hotspots to jump to concept)
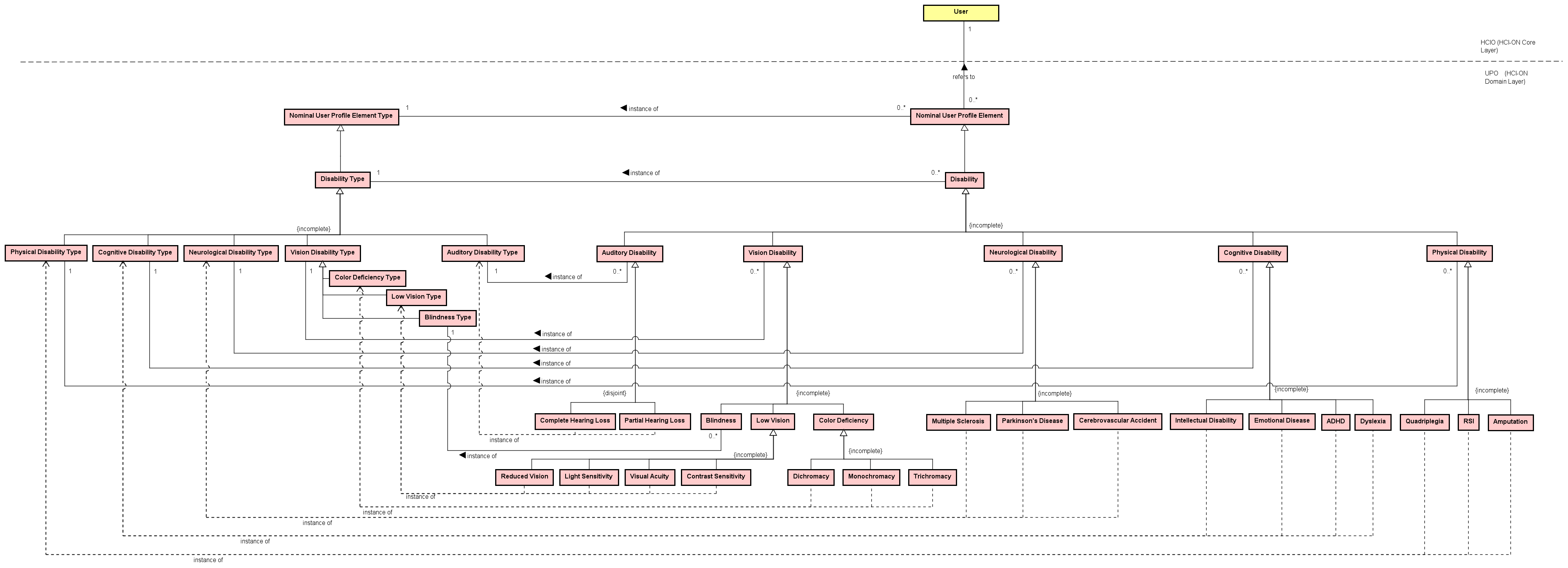 VDVision Disability - Blindness, Low Vision, Color Deficiency
BBlindness
LVLow Vision - Reduced Vision, Light Sensitivity, Visual Acuity, Contrast Sensitivity
CDColor Deficiency - Dichromacy, Monochromacy, Trichromacy
ADAuditory Disability - Complete or Partial Hearing Loss
CHLComplete Hearing Loss
PHLPartial Hearing Loss
CDCognitive Disability - Intellectual Disability, ADHD, Dyslexia, etc.
NDNeurological Disability - MS, Parkinson's, Stroke
PDPhysical Disability - RSI, Quadriplegia, Amputation
VDVision Disability - Blindness, Low Vision, Color Deficiency
BBlindness
LVLow Vision - Reduced Vision, Light Sensitivity, Visual Acuity, Contrast Sensitivity
CDColor Deficiency - Dichromacy, Monochromacy, Trichromacy
ADAuditory Disability - Complete or Partial Hearing Loss
CHLComplete Hearing Loss
PHLPartial Hearing Loss
CDCognitive Disability - Intellectual Disability, ADHD, Dyslexia, etc.
NDNeurological Disability - MS, Parkinson's, Stroke
PDPhysical Disability - RSI, Quadriplegia, Amputation
Figure 2: Disability Type taxonomy in UPO - vision, auditory, cognitive, neurological and physical categories and subtypes. (Click image to enlarge - click hotspots to jump to concept)
Concepts (UFO - Foundational Layer)
- Intrinsic Moment - Intrinsic Moments are moments that inhere in one single individual (e.g., an apple’s color). An example of an intrinsic moment is a Mode (@e.g., John’s desires, intentions, perceptions, symptoms, skills).
- Intrisic Moment Universal - It represents the type of a property that is inherent to a single entity and cannot exist independently of that entity (for example, the color of a car, the temperature of a person). Mode Universals and Quality Universals are subclassifications of Intrinsic Moment Universal.
- Mode - It represents an intrinsic and immeasurable characteristic of an individual, such as beliefs, skills, or thoughts, that cannot be quantified on a scale of values. E.g.: Alex's headache is a Mode, a property that exists only in Alex and cannot be measured or expressed in numerical terms.
- Mode Universal - It is an intrinsic universal moment that is not directly related to quality structures, that is, it denotes a non-measurable property. Its instances are called Modes, which are individual and non-qualitative properties that inhere in an Individual. Unlike qualities, modes cannot be represented in a quality structure or expressed in terms of measurable values. For example, Alex's headache is a Mode, a property that exists only in Alex and cannot be measured or expressed in numerical terms. Other examples of Universal Modes include Abilities, Beliefs, and Thoughts that have existential dependence on a single Individual.
- Person - A human Physical Agent. E.g.: Tim Berners Lee, Dennis Ritchie, Donald Knuth.
- Quale - It is the specific value within that Quality Structure that a Quality assumes for a particular Individual. E.g., if the Quality is a Person's Height, the point in the Quality Structure that represents that Height is the Quale. This value can be represented symbolically, such as the number 1.34 for Alex's height.
- Quality Universal - Quality Universals are those universals whose instances are Qualities. It denotes a measurable property. Examples include weight and height, which can characterize the universal concept of a person.
Concepts (HCIO - Core Layer)
- User - A Person who interacts with (or is expected to interact with) an Interactive Computer System.
Concepts (UPO - Domain Layer)
- Auditory Disability - hearing impairments (e.g., Complete or Partial Hearing Loss).
- Blindness - complete lack of vision.
- Cognitive Disability - limitations affecting cognition, planning or understanding (e.g., Intellectual Disability, ADHD, Dyslexia).
- Color Deficiency - conditions affecting color discrimination (e.g., dichromacy, monochromacy, trichromacy).
- Complete Hearing Loss - total deafness.
- Disability / Disability Type - disabilities the user may have; UPO models many disability categories (see taxonomy below).
- Gender / Gender Type - user's social identity/role (e.g., male, female).
- Language / Language Type - language(s) used by the user for communication (e.g., English).
- Low Vision - partial visual impairments (reduced acuity, light sensitivity).
- Measurable User Profile Element Type (examples) - these are types whose instances can be assigned values (User Profile Element Value):
- Age - the chronological age of the user (e.g., 40 years).
- Education Level - academic qualification (e.g., Bachelor's, Master's).
- Experience Level - user's familiarity with the system/technology (e.g., Basic, Average, High).
- Neurological Disability - disorders of nervous system causing mobility/cognitive issues (e.g., Multiple Sclerosis, Parkinson’s Disease, Cerebrovascular Accident).
- Nominal User Profile Element / Types - instances that refer to qualitative characteristics of a User:
- Gender / Gender Type - user's social identity/role (e.g., male, female).
- Language / Language Type - language(s) used by the user for communication (e.g., English).
- Disability / Disability Type - disabilities the user may have; UPO models many disability categories (see taxonomy below).
- Nominal User Profile Element - an instance that characterizes a particular User with respect to a Nominal User Profile Element Type (e.g., Alex’s Gender = male, Alex’s Language = English).
- Partial Hearing Loss - reduced hearing ability.
- Physical Disability - impairments affecting physical functioning, mobility or dexterity (e.g., Quadriplegia, RSI, Amputation).
- User Profile Element Type - a type of intrinsic characteristic that describes aspects of a User. UPO distinguishes two specializations:
- Measurable User Profile Element Type - quality-like types that allow assignment of numeric/ordered values (e.g., Age, Education Level, Experience Level).
- Nominal User Profile Element Type - qualitative types without a measurable scale (e.g., Language Type, Gender Type, Disability Type).
- User Profile Element Value - the actual value (a quale in UFO terms) assigned to a Measurable User Profile Element Type for a specific User. Examples from the instantiation: Alex’s Age = 40, Experience Level = Basic, Education Level = Bachelor’s degree.
- Vision Disability - impairments of the visual system (e.g., Blindness, Low Vision, Color Deficiency). Low Vision further specializes into Light Sensitivity, Reduced Vision, Visual Acuity, Contrast Sensitivity.
Instantiation example - Alex's case (UPO)
Instances extracted from the scenario used in the specification (Alex interacting with a social network system). These values illustrate how UPO represents a concrete user's profile.
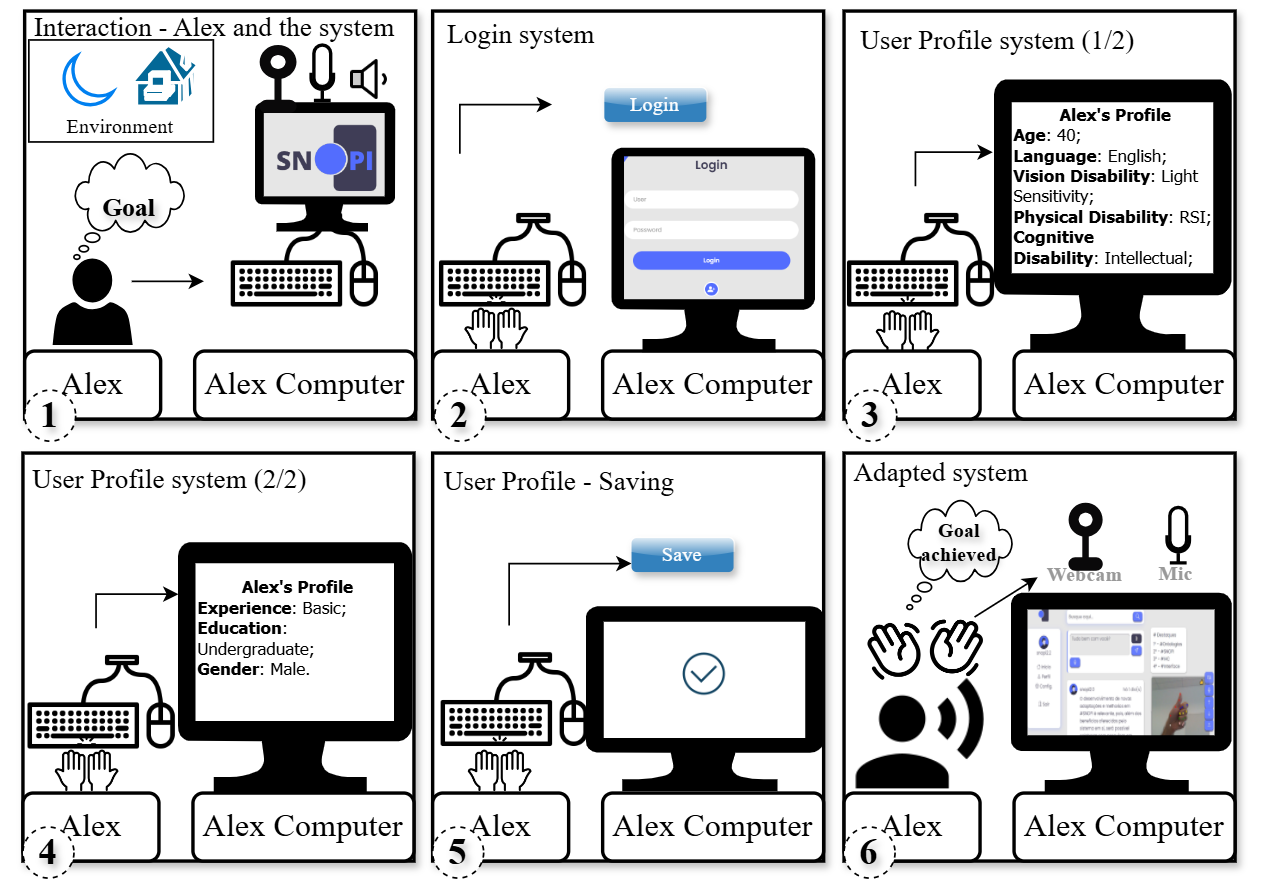
(Click to enlarge)
| Concept | Instance (Alex) |
|---|---|
| User | Alex |
| Nominal User Profile Element / Disability / Vision Disability / Low Vision | Light Sensitivity |
| Nominal User Profile Element / Disability / Physical Disability | Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) |
| Nominal User Profile Element / Disability / Cognitive Disability | Intellectual Disability |
| Nominal User Profile Element / Language | English |
| Nominal User Profile Element / Gender | Male |
| User Profile Element Value → Experience Level | Basic |
| User Profile Element Value → Education Level | Bachelor’s degree |
| User Profile Element Value → Age | 40 |
The ontologies were modeled in UML (Unified Modeling Language), but a specific representation of powertypes - when specializations of a concept are instances of another concept of a higher order - does not exist in UML. Thus, we used an adaptation (dotted arrow), following the approach for UML-based ontological modeling proposed by Guizzardi (2005), which allows for the dual nature of specializations to be adequately represented as instances of a higher-order concept within the ontology.
