The System and Software Ontology (SysSwO)
core ontology from SEON
SysSwO published paper1. Ontology Description
System and Software Ontology
3. Ontology Models
Figure 1 presents the packages of the SysSwO view HCIO.
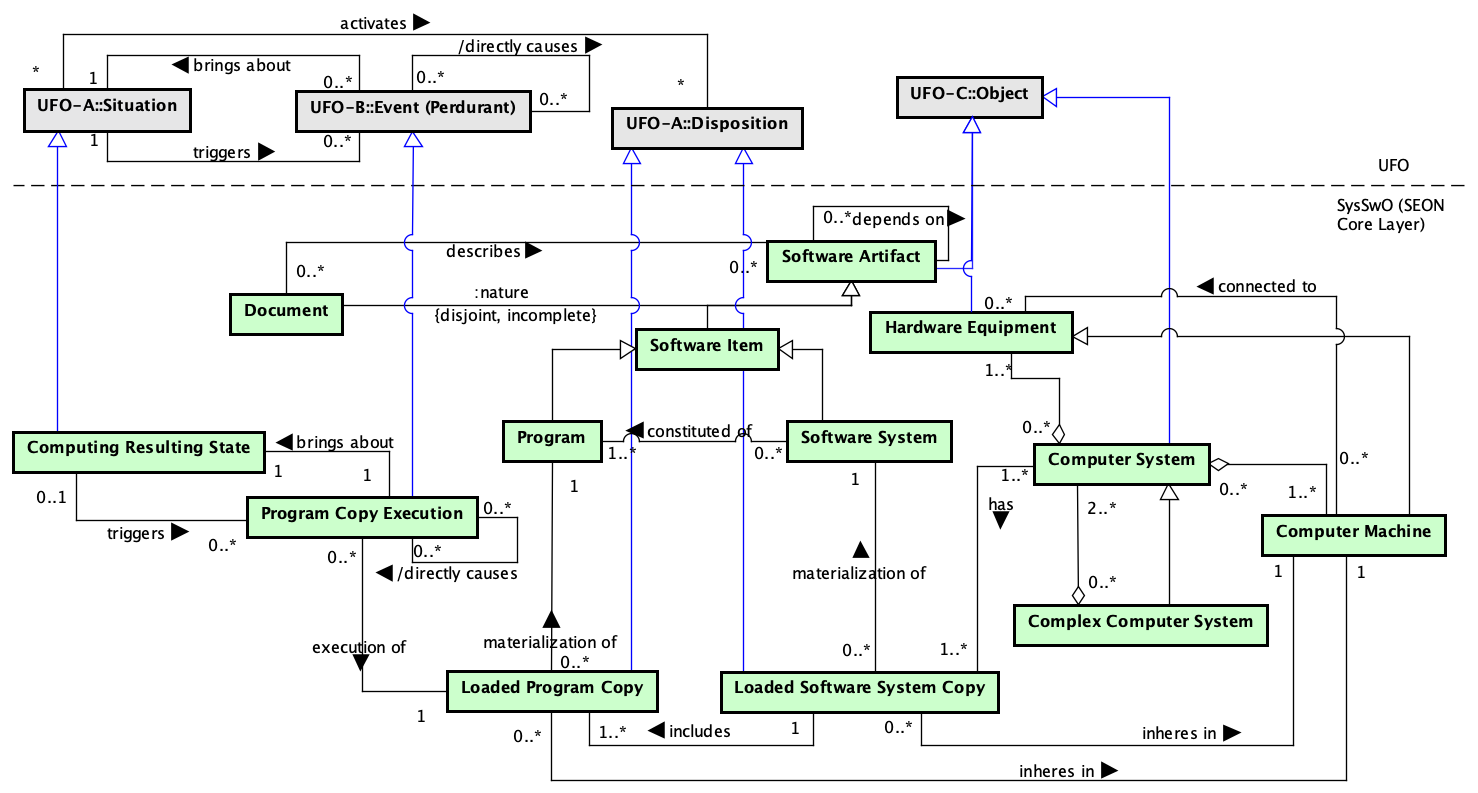
Figure 1. SysSwO view HCIO.
SysSwO is a core reference ontology (from SEON) about the nature of system and software, including, software artifacts, software constitution, software execution, computer system and hardware equipment.
Computer System is an Object combining hardware and software. Concerning hardware, a Computer System is composed of a set of Computer Machines. Computer Machine is a Hardware Equipment which other Hardware Equipment connect to it. Hardware Equipment is a physical Object used for running software programs or to support some software process activity (e.g., a printer, a router, a mouse, a keyboard).
Regarding software, a Computer System has a set of copies of software systems that are installed and loaded in the Computer Machines that comprise the Computer System. A copy of a software system installed and loaded in a Computer Machine is said a Loaded Software System Copy and it is a Disposition inhering in the Computer Machine where it is loaded. A Loaded Software System Copy is the materialization of a Software System, which is a subtype of Software Item. A Software Item, in turn, is a piece of software produced during the software development process, not considered a complete software product (e.g., a program).
A Software System is constituted of Programs (also a subtype of Software Item). Analogously to a Software System, to run a Program, one must have a copy of the program loaded in a Computer Machine (Loaded Program Copy) and execute it. Program Copy Execution is then an Event that brings about a particular Situation (the post-state of the event termed as a Computing Resulting State) resulting from the Program Copy Execution. A Computing Resulting State (Situation) can trigger other Program Copy Execution (Event). The Program Copy Execution (pce1) that brought about a Computing Resulting State that triggered a second Program Copy Execution (pce2) is said to directly cause it (pce1 directly causes pce2).
Finally, a Computer System can be composed of others Computer Systems. In this case, it is said a Complex Computer System.
3.1. Computer System
Figure 2 presents the conceptual model of the Computer System subontology.
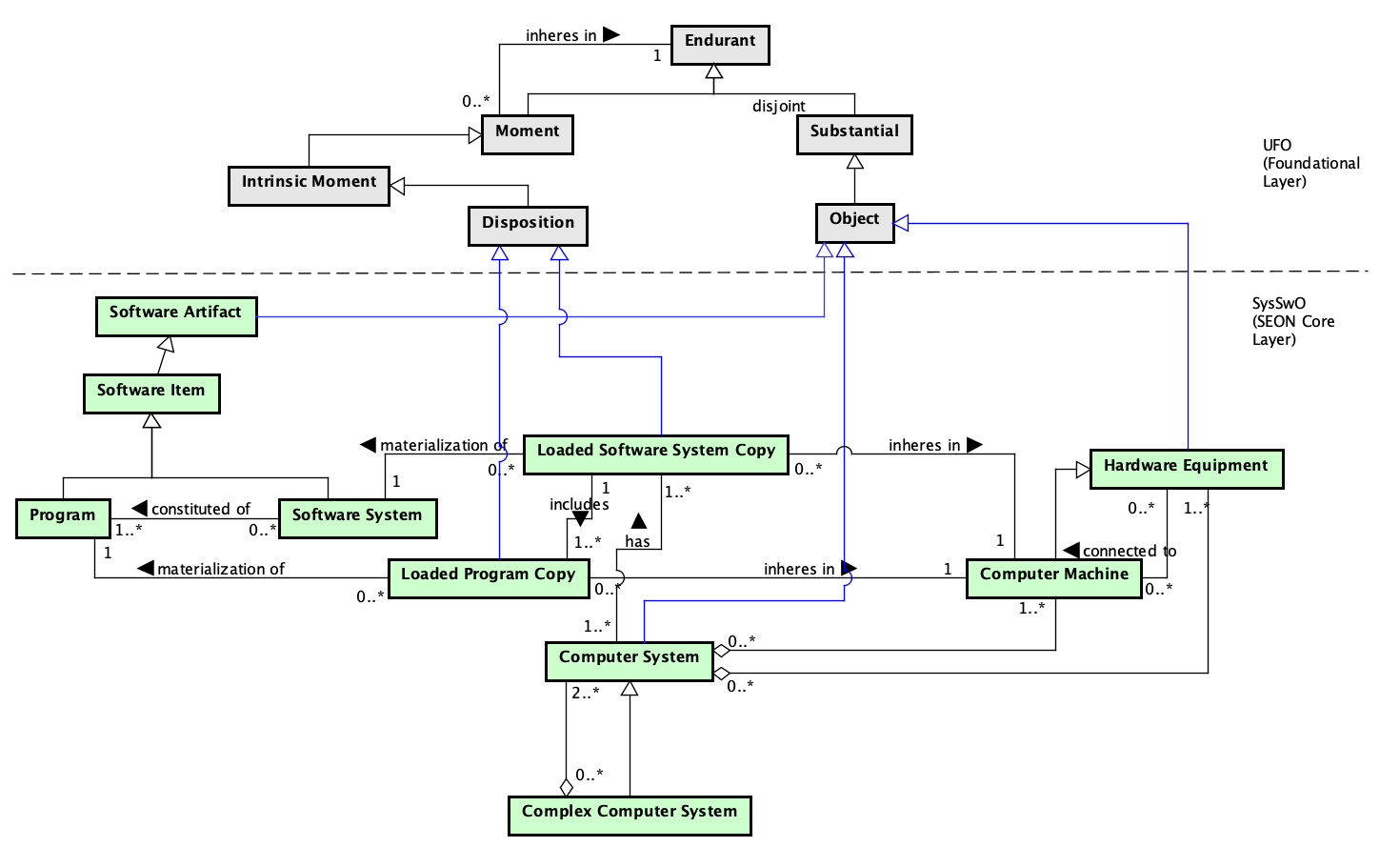
Figure 2. Computer System conceptual model.
3.2. Hw Equipment
Figure 3 presents the conceptual model of the Hw Equipment subontology.
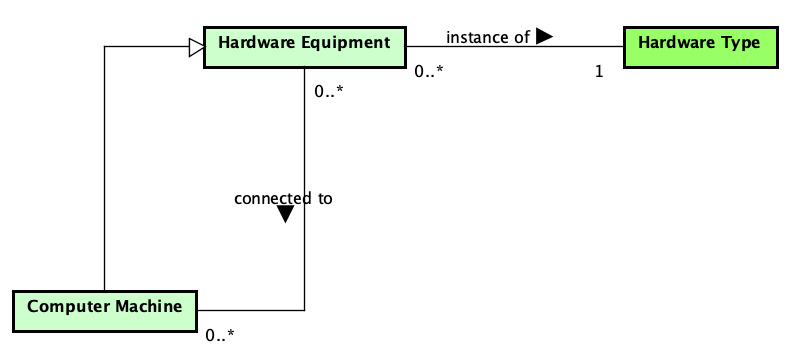
Figure 3. Hw Equipment conceptual model.
3.3. Program Execution
Figure 4 presents the conceptual model of the Program Execution subontology.
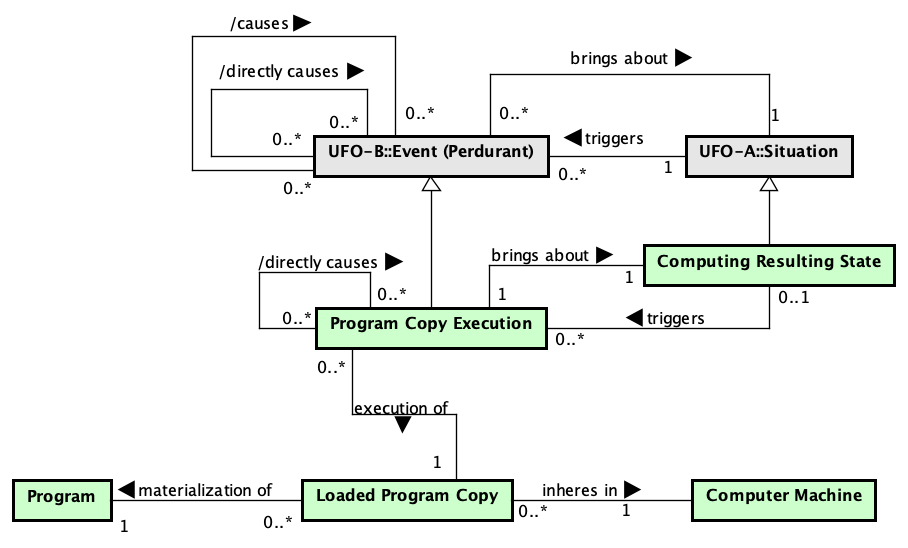
Figure 4. Program Execution conceptual model.
A Program is defined as a Software Item, a piece of software, produced during the software process, not considered a complete Software Product, but which aims at producing a certain result through execution on a computer, in a particular way, given by the Program Specification. In other words, a Program intends to implement a Program Specification, that intends to satisfy a set of Requirement Artifacts. Thus, we can say that there is a relation between Program and Requirement Artifact that is derived from the existing relation between Program Specification and Requirement Artifact.
A Loaded Program Copy is the materialization of a Program, inhering in a Machine. The Loaded Program Copy is a complex Disposition that is constituted by one or more Software Functions, which are, in turn, instances of Software Function Universals. When the software development process is accomplished correctly, the Software Functions that constitute the (loaded) program copy are instances of the exact Software Function Universals described by the Program Specification and successfully implemented by the Program.
Program Copy Execution is an Event representing the execution of the Loaded Program Copy running in a Machine, i.e., the Program Copy Execution is the event of the physical manifestation of the dispositions, represented as the complex disposition Loaded Program Copy, that inhere in the Machine. In this context, the Machine participates in the Program Copy Execution playing the role of Controller.
A Program Copy Execution, as an event, brings about a particular situation, said an Observable State. An Observable State is a situation resulting from the execution of a program copy.
3.4. Sw Artifacts
The Artifact Ontology aims at establishing a common conceptualization regarding Software Artifacts, including software products and related components.
Artifacts are objects consumed or produced during the software process. They can present different nature and composition. Possible types of Artifacts are (not limited to): Software Product (e.g. Eclipse IDE), Software Item (e.g. a database schema), Information Item (e.g. a bug reported), Model (e.g. a UML class model) and Document (e.g. a requirements specification). Documents can describe other Artifacts, as it is the case of a Design Specification describing a Software Architecture. The concepts Artifact Type, Document Type and Software Product Type define the possible specializations of Artifact, Software Product and Document (respectively).
An Artifact can be composite or simple. A Composite Artifact is composed of two or more other Artifacts (e.g. a Project Plan composed of artifacts as a WBS diagram and a Risk Plan). A Simple Artifact is not decomposable. Artifacts can also depend on other Artifacts to be produced or updated, such as a Test Case depending on the Code it was designed to test.
Figure 5 presents the conceptual model of the Sw Artifacts subontology.
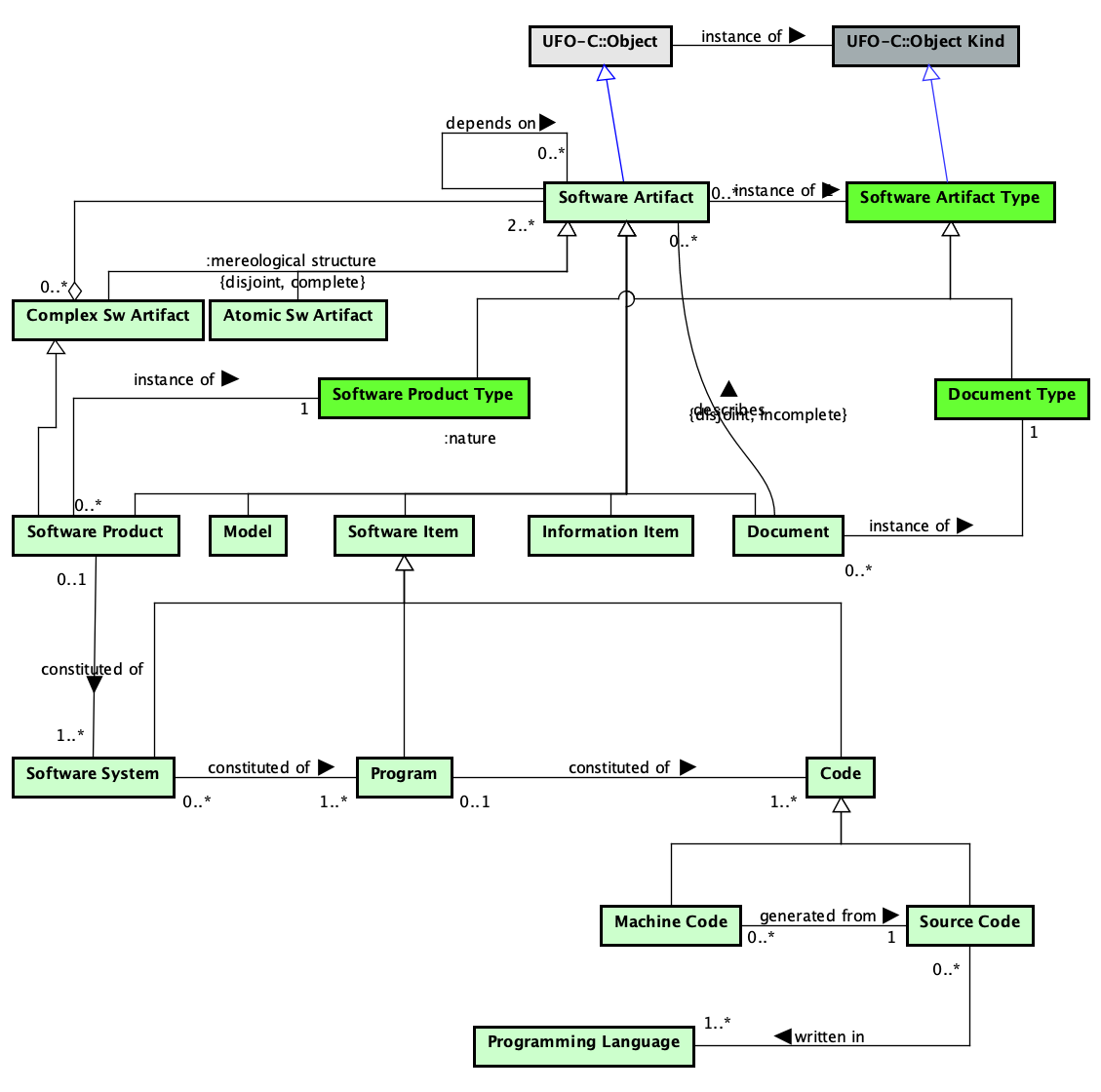
Figure 5. Sw Artifacts conceptual model.
In the context of the software domain, Artifacts are objects intentionally made to serve a given purpose in the context of a Software Project or Organization. They can be composed of other artifacts (Composite Artifact) or not (Simple Artifact). An artifact is an instance of an Artifact Type (a second order type). Artifact Type partitions the generalization set of Artifacts according to their nature, giving rise to a taxonomy of artifacts. More specific taxonomies can be established for specific types of artifacts, such as documents (established by instances of Document Type) and Software Product (Software Product Type), among others.
Figure 6 presents the packages of the Sw Constituition.
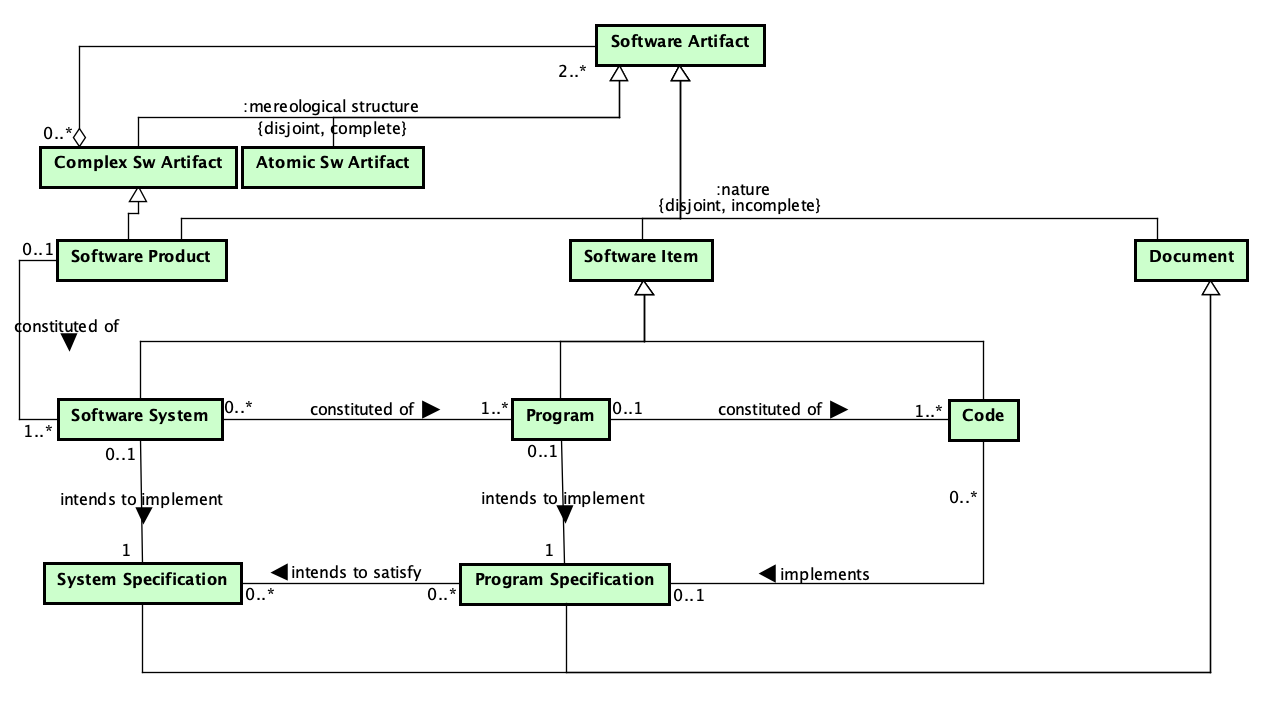
Figure 6. Sw Constituition.
The System and Software Ontology (SysSwO) captures that software products have a complex artifactual nature, being constituted of software artifacts of different nature, including software systems, programs and code.
4. Concepts Definition
The following table shows the definitions for SysSwO concepts.
| Concept | Definition |
|---|---|
Artifact that is not decomposed into other Artifacts. | |
Software Item representing a set of computer instructions and data definitions expressed in a programming language or in a form output by an assembler, compiler, or other translator (SEVOCAB). | |
Artifact composed of other Artifacts. | |
Hardware Equipment able to run programs, processing, transforming and storing data_____________Computer Machine is a hardware equipament able to run programs, processing, transforming and storing data and information.Definição ANTIGA: Machine is a hardware equipament able to run programs. | |
System containing one or more Computer Machines, and other Hardware Equipments connected to them, and associated software systems that are installed/loaded in these Machines (adapted from ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765:2017). | |
Observable State is a situation resulting from the execution of a program copy. It involves qualities and quality values (qualia) of the Machine in which the Loaded Program Copy inheres, as well as of entities residing in that Machine (including the Loaded Program Copy itself). | |
A Machine where a Loaded Program Copy is running (Program Copy Execution) plays the role of Controller. | |
Any written or pictorial, uniquely identified, information related to the software development, usually presented in a predefined format. | |
Artifact Type which is the powertype of Document, classifying its specializations. | |
DEFINIÇÃO NOVA: Physical Object used to process, transform, store, display or transmit information or dataDEFINIÇÃO ANTIGA: Physical Object used for running software programs or to support some related action. | |
Object Kind which is the powertype of Hardware Equipment, classifying its specializations. | |
Relevant information for human use, produced or used by Performed Activity. | |
Loaded Program Copy is the materialization of a Program, inhering in a Computer Machine. | |
Loaded Software System Copy is the materialization of a Software System, inhering in a Computer Machine. | |
Computer instructions and data definitions expressed in a form output by an assembler, compiler, or other translator, which can be recognized by the processing unit of a computer machine. | |
A representation (abstraction) of a process or system from a particular perspective. | |
Software Item which aims at producing a certain result through execution on a computer, in a particular way, given by the Program Specification. A Program is constituted by code, but it is not identical to code. Code can be changed without altering the identity of its program, which is anchored to the program's essential property: its intended specification (Program Specification). | |
Program Copy Execution is an Event representing the execution of the Loaded Program Copy running in a Machine. In other words, the Program Copy Execution is the event of the physical manifestation of the dispositions (represented as the complex disposition Loaded Program Copy) that inhere in the Machine. | |
A document that describes the purpose (structure and functions) of a program in sufficient detail to permit coding and to facilitate maintenance. | |
A language used to express computer programs. | |
Object intentionally made to serve a given purpose in the context of a software Project or Organization. | |
Object Kind which is the powertype of Artifact, classifying its specializations. | |
Software Functions are functional dispositions that constitute the complex disposition Loaded Program Copy. Each Software Function is an instance of a Software Function Universal. When the software development process is accomplished correctly, the Software Functions that constitute the Loaded Program Copy are instances of the exact Software Function Universals described by the Program Specification and successfully implemented by the Program. | |
Piece of software, produced during the software process, not considered a complete Software Product, but an intermediary result. | |
One or more computer programs together with any accompanying auxiliary items, such as documentation, delivered under a single name, ready for use. | |
Artifact Type which is the powertype of Software Product, classifying its specializations. | |
Software Item that aims at satisfying a specification (System Specification), concerning a desired change in a data structure inside a computer, abstracting away from the behavior. | |
A well-formed sequence of computer instructions and data definitions expressed in a programming language, in a form suitable for input to an assembler, compiler,or other translator. | |
5. Detailed Concepts
System and Software Ontology (SysSwO) detailed concepts.
SysSwO::Atomic Sw Artifact
<<category>>
Atomic Sw Artifact
Specializes:
SysSwO::Software Artifact
Definition:
Artifact that is not decomposed into other Artifacts.
Relations:
SysSwO::Code
<<subkind>>
Code
Specializes:
SysSwO::Software Item
Definition:
Software Item representing a set of computer instructions and data definitions expressed in a programming language or in a form output by an assembler, compiler, or other translator (SEVOCAB).
Relations:
Code (0..*) implements (0..1) Program Specification
Code Documentation changes Code
Code Development creates Code
Program (0..1) constituted of (1..*) Code
Code Review uses Code
SysSwO::Complex Computer System
Complex Computer System
Specializes:
SysSwO::Computer System
Definition:
Relations:
Complex Computer System (0..*) <>-- (2..*) Computer System
SysSwO::Complex Sw Artifact
<<category>>
Complex Sw Artifact
Specializes:
SysSwO::Software Artifact
Definition:
Artifact composed of other Artifacts.
Relations:
Complex Sw Artifact (0..*) <>-- (2..*) Software Artifact <<componentOf>>
SysSwO::Computer Machine
Computer Machine
Specializes:
SysSwO::Hardware Equipment
Definition:
Hardware Equipment able to run programs, processing, transforming and storing data_____________Computer Machine is a hardware equipament able to run programs, processing, transforming and storing data and information.Definição ANTIGA: Machine is a hardware equipament able to run programs.
Relations:
Computer Machine (0..*) connected to (0..*) Hardware Equipment
Computer System (0..*) <>-- (1..*) Computer Machine
Loaded Software System Copy (0..*) inheres in (1..1) Computer Machine
Loaded Program Copy (0..*) inheres in (1..1) Computer Machine
SysSwO::Computer System
Computer System
Specializes:
UFO::Object
Definition:
System containing one or more Computer Machines, and other Hardware Equipments connected to them, and associated software systems that are installed/loaded in these Machines (adapted from ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765:2017).
Relations:
Computer System (0..*) <>-- (1..*) Computer Machine
Computer System (0..*) <>-- (1..*) Hardware Equipment
Computer System (1..*) has (1..*) Loaded Software System Copy
Complex Computer System (0..*) <>-- (2..*) Computer System
SysSwO::Computing Resulting State
Computing Resulting State
Specializes:
UFO::Situation
Definition:
Observable State is a situation resulting from the execution of a program copy. It involves qualities and quality values (qualia) of the Machine in which the Loaded Program Copy inheres, as well as of entities residing in that Machine (including the Loaded Program Copy itself).
Relations:
Computing Resulting State (0..1) triggers (0..*) Program Copy Execution
Computing Resulting State (0..*) satisfies (0..*) Mental Computing Resulting State
User Interface shows Computing Resulting State
Program Copy Execution (1..1) brings about (1..1) Computing Resulting State
SysSwO::Controller
Controller
Specializes:
SysSwO::Computer Machine
Definition:
A Machine where a Loaded Program Copy is running (Program Copy Execution) plays the role of Controller.
Relations:
Controller (1..1) participates in (1..*) Program Copy Execution
SysSwO::Document
<<kind>>
Document
Specializes:
SysSwO::Software Artifact
Definition:
Any written or pictorial, uniquely identified, information related to the software development, usually presented in a predefined format.
Example: a Requirements Document, a specification, a report.
Relations:
Document (0..*) describes (0..*) Software Artifact
Document (0..*) instance of (1..1) Document Type
SysSwO::Document Type
<<2ndOT>>
Document Type
Specializes:
SysSwO::Software Artifact Type
Definition:
Artifact Type which is the powertype of Document, classifying its specializations.
Example: Requirements Document, Design Specification, Project Plan.
Relations:
Document Template (0..*) applies to (1..1) Document Type
Document (0..*) instance of (1..1) Document Type
SysSwO::Hardware Equipment
<<kind>>
Hardware Equipment
Specializes:
UFO::Object
Definition:
DEFINIÇÃO NOVA: Physical Object used to process, transform, store, display or transmit information or dataDEFINIÇÃO ANTIGA: Physical Object used for running software programs or to support some related action.
Example: Computer Dell I7, Laser Printer HP, Smartphone Galaxy 7, Router Linksys Wi-fi.
Relations:
Hardware Equipment (0..*) instance of (1..1) Hardware Type
Computer System (0..*) <>-- (1..*) Hardware Equipment
Computer Machine (0..*) connected to (0..*) Hardware Equipment
User Interface <>-- Hardware Equipment
Interactive Computer System <>-- Hardware Equipment
SysSwO::Hardware Type
<<2ndOT>>
Hardware Type
Specializes:
UFO::Object Kind
Definition:
Object Kind which is the powertype of Hardware Equipment, classifying its specializations.
Example: Computer, Printer, Router, Keyboard.
Relations:
Intended Activity (0..*) requires (0..*) Hardware Type
Hardware Equipment (0..*) instance of (1..1) Hardware Type
Standard Activity (0..*) requires (0..*) Hardware Type
SysSwO::Information Item
<<kind>>
Information Item
Specializes:
SysSwO::Software Artifact
Definition:
Relevant information for human use, produced or used by Performed Activity.
Example: a documented requirement, a bug reported, an agreement e-mail, a component description.
Relations:
SysSwO::Loaded Program Copy
Loaded Program Copy
Specializes:
UFO::Disposition
Definition:
Loaded Program Copy is the materialization of a Program, inhering in a Computer Machine.
Example: a copy of a program loaded in primary memory of my computer.
Relations:
Loaded Program Copy (0..*) materialization of (1..1) Program
Loaded Program Copy (1..1) constituted by (1..*) Software Function
Loaded Program Copy (0..*) inheres in (1..1) Computer Machine
Loaded Program Copy (1..*) handles (0..1) User Interface
Loaded Software System Copy (1..1) includes (1..*) Loaded Program Copy
Program Copy Execution (0..*) execution of (1..1) Loaded Program Copy
SysSwO::Loaded Software System Copy
Loaded Software System Copy
Specializes:
UFO::Disposition
Definition:
Loaded Software System Copy is the materialization of a Software System, inhering in a Computer Machine.
Example: a copy of a software system loaded in the primary memory of my computer.
Relations:
Loaded Software System Copy (0..*) materialization of (1..1) Software System
Loaded Software System Copy (0..*) inheres in (1..1) Computer Machine
Loaded Software System Copy (1..1) includes (1..*) Loaded Program Copy
Computer System (1..*) has (1..*) Loaded Software System Copy
SysSwO::Machine Code
<<subkind>>
Machine Code
Specializes:
SysSwO::Code
Definition:
Computer instructions and data definitions expressed in a form output by an assembler, compiler, or other translator, which can be recognized by the processing unit of a computer machine.
Relations:
Machine Code (0..*) generated from (1..1) Source Code
SysSwO::Model
<<kind>>
Model
Specializes:
SysSwO::Software Artifact
Definition:
A representation (abstraction) of a process or system from a particular perspective.
Example: a use case model, a class model, a component model.
Relations:
SysSwO::Program
<<subkind>>
Program
Specializes:
SysSwO::Software Item
Definition:
Software Item which aims at producing a certain result through execution on a computer, in a particular way, given by the Program Specification. A Program is constituted by code, but it is not identical to code. Code can be changed without altering the identity of its program, which is anchored to the program's essential property: its intended specification (Program Specification).
Relations:
Program (0..1) constituted of (1..*) Code
Program (0..1) intends to implement (1..1) Program Specification
Program (0..*) implements (1..*) Software Function Universal
Program (0..*) \intends to satisfy (1..*) Requirement Artifact
Program (0..*) implements (0..*) Quality Characteristic
Software System (0..*) constituted of (1..*) Program
Loaded Program Copy (0..*) materialization of (1..1) Program
SysSwO::Program Copy Execution
Program Copy Execution
Specializes:
UFO::Event (Perdurant)
Definition:
Program Copy Execution is an Event representing the execution of the Loaded Program Copy running in a Machine. In other words, the Program Copy Execution is the event of the physical manifestation of the dispositions (represented as the complex disposition Loaded Program Copy) that inhere in the Machine.
Relations:
Program Copy Execution (0..*) execution of (1..1) Loaded Program Copy
Program Copy Execution (1..1) brings about (1..1) Computing Resulting State
Program Copy Execution (1..1) /directly causes (0..*) User Interpretation
Program Copy Execution (0..*) /directly causes (0..*) Program Copy Execution
Computing Resulting State (0..1) triggers (0..*) Program Copy Execution
User Initiated Participation (0..1) /directly causes (0..*) Program Copy Execution
User Input Resulting State (0..1) triggers (0..*) Program Copy Execution
Controller (1..1) participates in (1..*) Program Copy Execution
Interactive Computer System Participation (1..1) <>-- (0..*) Program Copy Execution
SysSwO::Program Specification
<<subkind>>
Program Specification
Specializes:
SysSwO::Document
Definition:
A document that describes the purpose (structure and functions) of a program in sufficient detail to permit coding and to facilitate maintenance.
Relations:
Program Specification (0..*) intends to satisfy (0..*) System Specification
Program Specification (0..*) intends to satisfy (1..*) Requirement Artifact
Program Specification (0..*) describes (1..*) Software Function Universal
Program (0..1) intends to implement (1..1) Program Specification
Code (0..*) implements (0..1) Program Specification
SysSwO::Programming Language
<<kind>>
Programming Language
Specializes:
UFO::Social Object
Definition:
A language used to express computer programs.
Relations:
Source Code (0..*) written in (1..*) Programming Language
SysSwO::Software Artifact
<<category>>
Software Artifact
Specializes:
RSMO::Measurable Software-Related Entity
UFO::Object
Definition:
Object intentionally made to serve a given purpose in the context of a software Project or Organization.
Example: a document, a model, a library, an e-mail, a bug.
Relations:
Software Artifact (0..*) instance of (1..1) Software Artifact Type
Software Artifact (0..*) depends on Software Artifact <<material>>
Artifact Participation (0..*) participation of (1..1) Software Artifact
Document (0..*) describes (0..*) Software Artifact
Complex Sw Artifact (0..*) <>-- (2..*) Software Artifact <<componentOf>>
Performed Activity (1..1) creates (0..*) Software Artifact <<material>>
Performed Activity (0..*) changes (0..*) Software Artifact
Performed Activity (0..*) uses (0..*) Software Artifact
Stakeholder (0..*) responsible for (0..*) Software Artifact <<material>>
SysSwO::Software Artifact Type
<<2ndOT>>
Software Artifact Type
Specializes:
UFO::Object Kind
Definition:
Object Kind which is the powertype of Artifact, classifying its specializations.
Example: Document, Model, Software Product, Information Item, Software Item.
Relations:
Intended Activity (0..*) creates (0..*) Software Artifact Type
Intended Activity (0..*) changes (0..*) Software Artifact Type
Intended Activity (0..*) uses (0..*) Software Artifact Type
Software Artifact (0..*) instance of (1..1) Software Artifact Type
Standard Activity (0..*) uses (0..*) Software Artifact Type
Standard Activity (0..*) changes (0..*) Software Artifact Type
Standard Activity (0..*) creates (0..*) Software Artifact Type
SysSwO::Software Function
Software Function
Specializes:
UFO::Function
Definition:
Software Functions are functional dispositions that constitute the complex disposition Loaded Program Copy. Each Software Function is an instance of a Software Function Universal. When the software development process is accomplished correctly, the Software Functions that constitute the Loaded Program Copy are instances of the exact Software Function Universals described by the Program Specification and successfully implemented by the Program.
Relations:
Software Function (0..*) instance of (1..*) Software Function Universal
Loaded Program Copy (1..1) constituted by (1..*) Software Function
SysSwO::Software Item
<<kind>>
Software Item
Specializes:
SysSwO::Software Artifact
UFO::Object
Definition:
Piece of software, produced during the software process, not considered a complete Software Product, but an intermediary result.
Example: a component, database schema, a script.
Relations:
SysSwO::Software Product
<<kind>>
Software Product
Specializes:
SysSwO::Software Artifact
SysSwO::Complex Sw Artifact
Definition:
One or more computer programs together with any accompanying auxiliary items, such as documentation, delivered under a single name, ready for use.
Example: Astah modeling tool, Microsoft Word, Eclipse IDE.
Relations:
Software Product (0..*) instance of (1..1) Software Product Type
Software Product (0..1) constituted of (1..*) Software System
User Interface <>-- Software Product
SysSwO::Software Product Type
<<2ndOT>>
Software Product Type
Specializes:
SysSwO::Software Artifact Type
Definition:
Artifact Type which is the powertype of Software Product, classifying its specializations.
Example: Modeling Tool, Text Editor, IDE, Compiler.
Relations:
Intended Activity (0..*) requires (0..*) Software Product Type
Software Product (0..*) instance of (1..1) Software Product Type
Standard Activity (0..*) requires (0..*) Software Product Type
SysSwO::Software System
<<subkind>>
Software System
Specializes:
SysSwO::Software Item
Definition:
Software Item that aims at satisfying a specification (System Specification), concerning a desired change in a data structure inside a computer, abstracting away from the behavior.
Relations:
Software System (0..*) constituted of (1..*) Program
Software System (0..1) intends to implement (1..1) System Specification
Software Product (0..1) constituted of (1..*) Software System
Loaded Software System Copy (0..*) materialization of (1..1) Software System
SysSwO::Source Code
<<subkind>>
Source Code
Specializes:
SysSwO::Code
Definition:
A well-formed sequence of computer instructions and data definitions expressed in a programming language, in a form suitable for input to an assembler, compiler,or other translator.
Relations:
Source Code (0..*) written in (1..*) Programming Language
Machine Code (0..*) generated from (1..1) Source Code
SysSwO::System Specification
<<subkind>>
System Specification
Specializes:
SysSwO::Document
Definition:
Relations:
Software System (0..1) intends to implement (1..1) System Specification
Program Specification (0..*) intends to satisfy (0..*) System Specification