The Human-Computer Interaction Evaluation Ontology (HCIEO)
domain ontology from HCI-ON
1. Ontology Description
The Human-Computer Interaction Evaluation Ontology (HCIEO), a reference ontology that aims to provide a common conceptualization of HCI Evaluation and is a domain ontology of HCI-ON.
The purpose of the HCI Evaluation Ontology (HCIEO) is to establish an explicit and shared conceptualization of HCI evaluation by means of a human-centred design view, describing the main concepts involved in this context.
HCIEO covers relevant aspects of the HCI evaluation, such as the main involved artifacts, considered evaluation criteria, evaluated characteristics, involved agents and measures that can be used to evaluate an interactive computer system.
3. Ontology Models
Figure 1 presents the packages of the HCIEO Modularization.
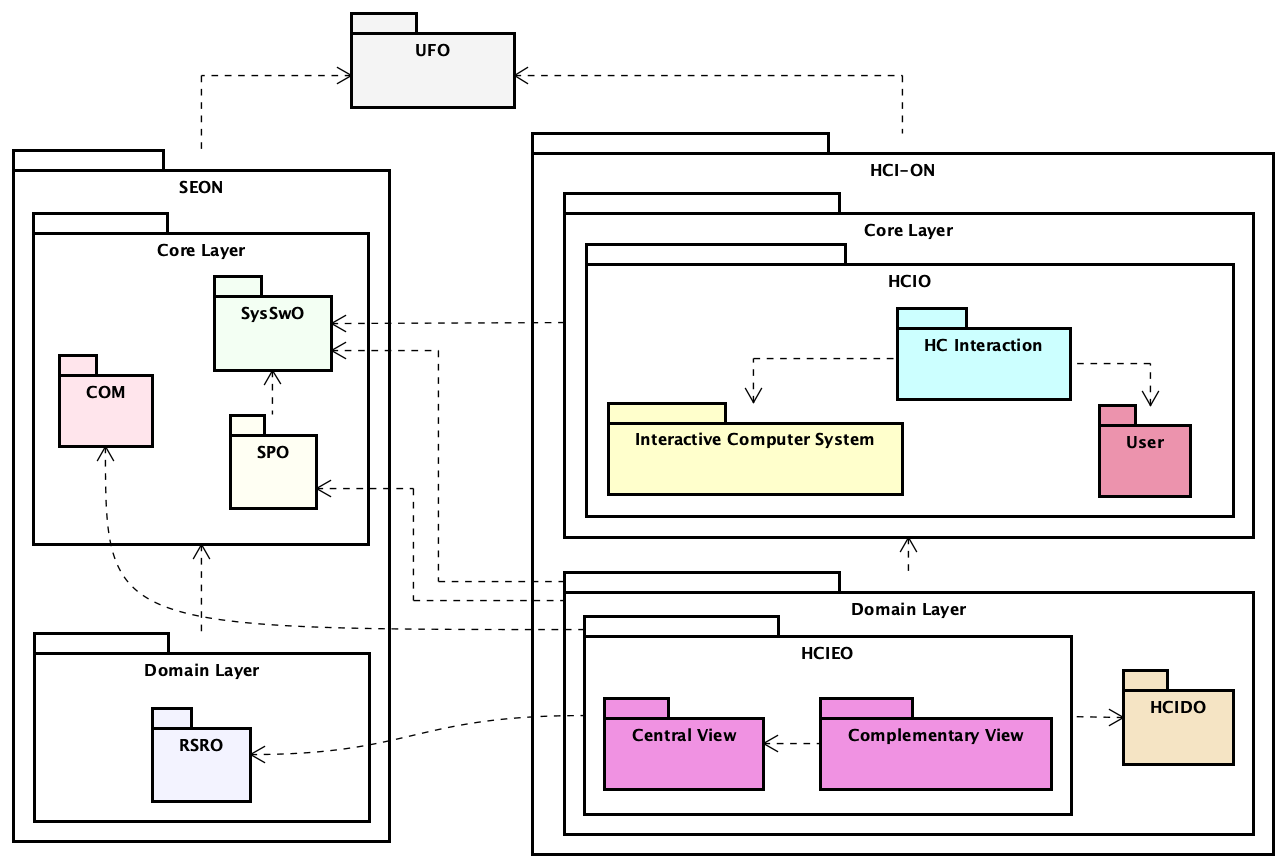
Figure 1. HCIEO Modularization.
3.1. Central View
Figure 2 presents the conceptual model of the HCIEO Central View subontology.
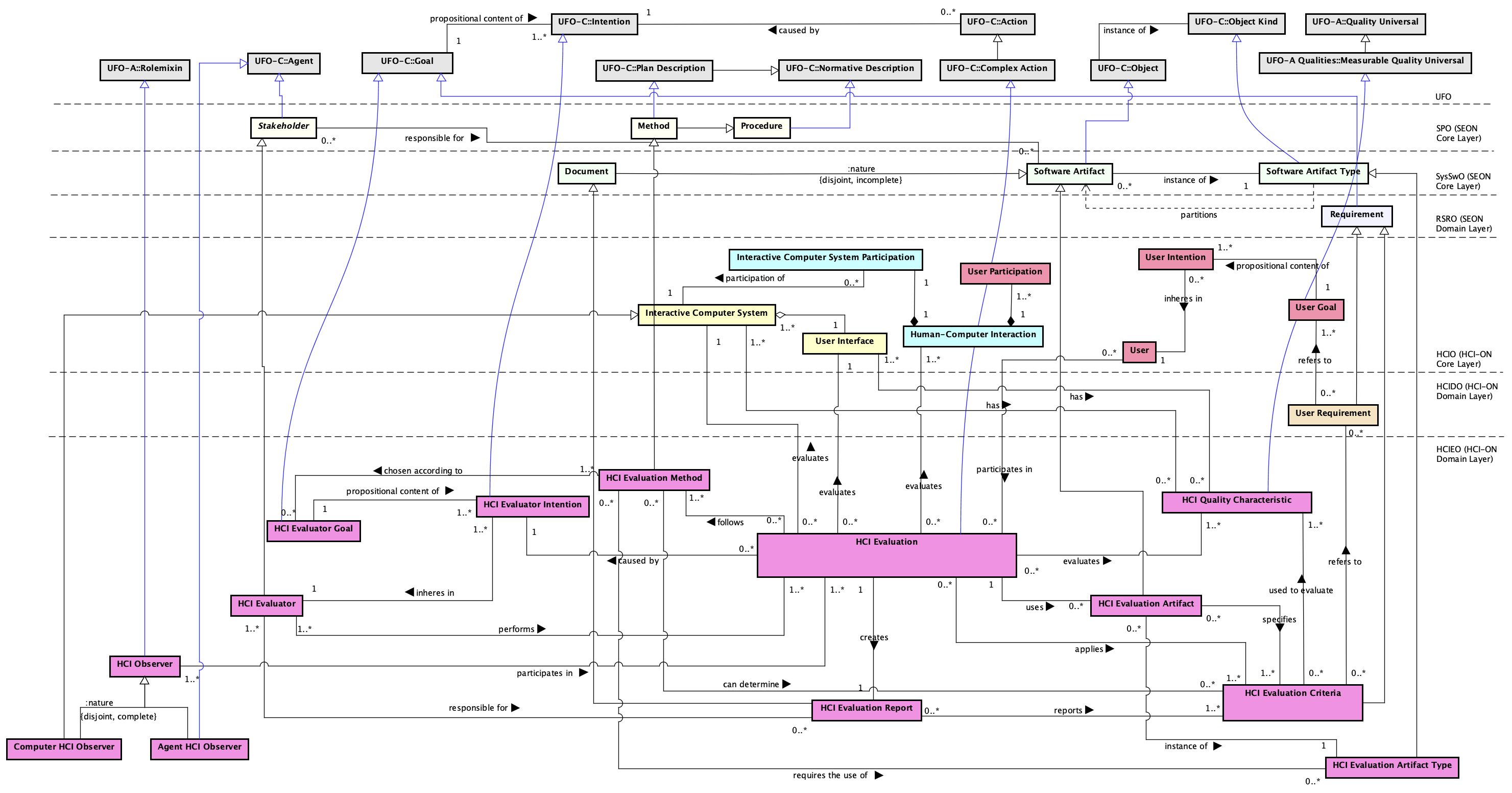
Figure 2. HCIEO Central View conceptual model.
HCI Evaluation is a Complex Action and, like that, it is an intentional event. It is caused by the HCI Evaluator Intention that inheres in the HCI Evaluator. Being an Intention, HCI Evaluator Intention has a HCI Evaluator Goal (Goal) as propositional content. HCI Evaluator is the role played by an individual or an organization (Stakeholder) that performs the HCI Evaluation.
HCI Observer participates in HCI Evaluations and is responsible for getting data through observation. HCI Observer is a Rolemixin, thus it aggregates role types whose instances have different identity principles (nature). Therefore, when an agent (Agent) plays the HCI Observer role, it is an Agent HCI Observer. When observation is made by an Interactive Computer System (e.g., by capturing interaction data and storing it an interaction log file), the HCI Observer is a Computer HCI Observer.
An HCI Evaluation consists in the systematic determination of the extent to which an Interactive Computer System’s (or its User Interface) quality characteristics (HCI Quality Characteristic) meet the HCI Evaluation Criteria applied in the evaluation. HCI Evaluation Criteria, in turn, are conditions, or capacity needed (Requirement), used to evaluate Interactive Computer System’s HCI Quality Characteristics and may be related to User Requirements.
HCI Quality Characteristics are qualities (Quality Universal) of an Interactive Computer System (manifested in its software or hardware constituents). Therefore, HCI Evaluation evaluates HCI Quality Characteristics of an Interactive Computer System or, more specifically, of its User Interface. Thus, the following axioms apply:
A6.1. ∀ hcie: HCI Evaluation, ics: Interactive Computer System, hciqc: HCI Quality Characteristic evaluates(hcie, ics) ∧ evaluates(hcie, hciqc) → has(ics, hciqc)
A6.2. ∀ hcie: HCI Evaluation, ui: User Interface, hciqc: HCI Quality Characteristic evaluates(hcie, ui) ∧ evaluates(hcie, hciqc) → has(ui, hciqc)
An HCI Evaluation follows an HCI Evaluation Method (e.g., Heuristic Method, Usability Testing), which is a Method that describes the actions to be performed by the HCI Evaluator in an HCI Evaluation. An HCI Evaluation Method is chosen according to the HCI Evaluator Goal and can determine the HCI Evaluation Criteria to be applied in an HCI Evaluation. Moreover, an HCI Evaluation Method may require the use of HCI Evaluation Artifact Types (e.g., HCI evaluation checklist). Thus, to perform an HCI Evaluation it may be necessary to use HCI Evaluation Artifacts (Software Artifact), which are objects intentionally built to specify, among others, the HCI Evaluation Criteria to be applied in the evaluation (e.g., a checklist specifying the criteria to be applied). The HCI Evaluation Artifacts used in an HCI Evaluation should be instances of the HCI Evaluation Artifact Types required by the HCI Evaluation Method used in that HCI Evaluation. For example, if an HCI evaluation used an HCI evaluation method which requires a kind of HCI evaluation checklist, then that evaluation should have used a particular HCI evaluation checklist (i.e., an instance of the HCI evaluation checklist required by the adopted method. Thus, the following axiom applies:
A6.3. ∀ hcie: HCI Evaluation, m: HCI Evaluation Method, at: HCI Evaluation Artifact Type follows(hcie, m) ∧ requiresTheUseOf(m, at) → ∃ a: HCI Evaluation Artifact uses(hcie, a) ∧ isInstanceOf(a, at)
In some HCI Evaluations it is necessary to evaluate the Interactive Computer System during the Human-Computer Interaction. In this case, the User (or user representatives) of the Interactive Computer System participates in the HCI Evaluation while, at the same time, participates (User Participation), together with the Interactive Computer System (Interactive Computer System Participation), in the Human-Computer Interaction. When the User participates in an HCI Evaluation, it is required that this User uses the Interactive Computer System in order to achieve a certain goal (User Goal) (e.g., send an email). While the User interacts with the Interactive Computer System to achieve his/her goal (User Goal), the HCI Evaluator performs the HCI Evaluation, following the HCI Evaluation Method and applying HCI Evaluation Criteria to evaluate HCI Quality Characteristics of the Interactive Computer System. This scenario involves some constraints, addressed by the following axioms:
A6.4. ∀ hcie: HCI Evaluation, ics: Interactive Computer System, icsp: Interactive Computer System Participation, hci: Human-Computer Interaction, user: User evaluates(hcie, ics) ∧ participatesIn(user, hcie) ∧ composedOf(hci, icsp) → ∃ up: User Participation participationOf (user, up) ∧ composedOf(hci, up)
A6.5. ∀ hcie: HCI Evaluation, hci: Human-Computer Interaction, hciqc: HCI Quality Characteristic, ics: Interactive Computer System, icsp: Interactive Computer System Participation evaluates(hcie, hci) ∧ evaluates(hcie, hciqc) ∧ has(ics, hciqc) ∧ composedOf(hci, icsp) ∧ participationOf(icsp, ics) → evaluates(hcie, ics)
Moreover, in an HCI Evaluation an HCI Evaluator can act as a User. Conversely, a User can act as an HCI Evaluator. Thus, if an evaluator performs an evaluation in which he/she acts as a user, then this evaluator is also the user who participates in the evaluation. On the other hand, if a user that participates in an evaluation performs that evaluation, then he/she is also an evaluator of that evaluation. Hence, the following axioms apply:
A6.6. ∀ e: HCI Evaluator, hcie: HCI Evaluation performs(e, hcie) ∧ participatesIn(e, hcie) → ∃ u: User participatesIn(u, hcie) ∧ (e = u)
A6.7. ∀ u: User, hcie: HCI Evaluation participatesIn(u, hcie) ∧ performs(u, hcie) → ∃ e: HCI Evaluator performs(e, hcie) ∧ (e = u)
After the HCI Evaluation is performed, the HCI Evaluation Report, a Document, is created, under the responsibility of the HCI Evaluator, aiming to report the evaluation results and other relevant information, such as the applied HCI Evaluation Criteria. The HCI Evaluation Report is a Document, i.e., any written or pictorial information usually presented in a predefined format. Therefore, it can refer to, for example a description of the results registered in a textual form or a slides presentation, among others. If an HCI Evaluation has more than one HCI Evaluator, at least one of them must be responsible for the HCI Evaluation Report. Thus:
A6.8. ∀ hcie: HCI Evaluation, er: HCI Evaluation Report creates(hcie, er) → ∃ e: HCI Evaluator performs(e, hcie) ∧ responsibleFor(e, er)
3.2. Complementary View
Figure 3 presents the conceptual model of the HCIEO Complementary View subontology.
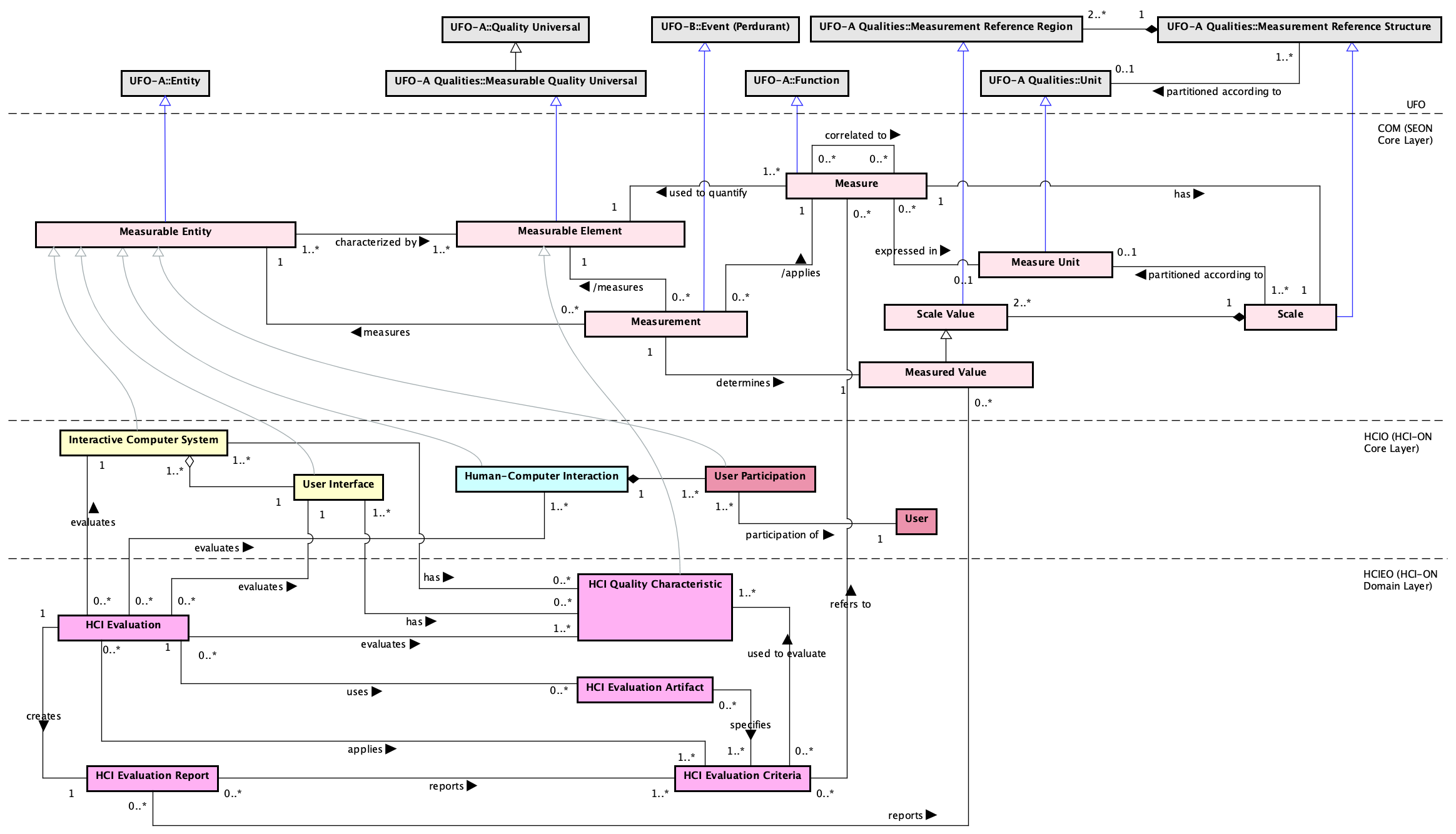
Figure 3. HCIEO Complementary View conceptual model.
There are HCI Evaluations in which it is necessary to perform measurements to determine the extent to which HCI Quality characteristics of an Interactive Computer System meet HCI Evaluation Criteria. This is addressed in the conceptual model shown in Figure 3, which depicts a view of HCIEO that reuses concepts from COM to represent evaluations that quantify HCI Quality Characteristics. As in Figure 2, at the top we have UFO. At the center, there are COM (SEON Core Layer), containing core concepts related to measurement, and HCIO (HCI-ON Core Layer), providing HCI core concepts. At the bottom, there are HCIEO concepts, representing a complementary view of Figure 2 to complement the HCIEO conceptual model.
In the HCIEO and HCIO conceptual models, Interactive Computer System and User Interface are Objects in UFO while Human-Computer Interaction and User Participation are Actions. In COM, both Object and Action are subtype of Measurable Entity. Thus, in Figure 3 the generalization relations from Measurable Entity shown in light gray are just to illustrate that being Objects or Actions in UFO, Interactive Computer System and User Interface, Human-Computer Interaction and User Participation also are Measurable Entities. Moreover, in the model shown in Figure 3, we focus on HCI Quality Characteristics that are quantified by some Measure. Thus, the generalization relation from Measurable Element shown in light gray is just to illustrate that in that context, HCI Quality Characteristic is a subtype of Measurable Element.
Besides being Objects (grounding in UFO), Interactive Computer System and User Interface are also Measurable Entities, i.e., entities that can be measured. In this sense, HCI Quality Characteristic is subtype of Measurable Element, i.e., a measurable property that characterizes Interactive Computer System (or a User Interface). Measures can be used to quantify HCI Quality Characteristics. For example, usability (HCI Quality Characteristic) characterizes a system (Interactive Computer System) or its UI (User Interface) and can be quantified, among others, by means of the number of wrong clicks or touches (Measure). HCI Evaluation Criteria can refer to Measures used to quantify HCI Quality Characteristic. For example, the criteria “the number of wrong clicks or touches must be smaller than two”, used to evaluate usability, refers to the measure number of wrong clicks or touches, which, in turn, is used to quantify usability. In this context, the Measure referred by an HCI Evaluation Criteria in an HCI Evaluation that evaluates an HCI Quality Characteristic must be a Measure used to quantify that HCI Quality Characteristic. Thus:
A6.9. ∀ m: Measure, hciec: HCI Evaluation criteria, hcie: HCI Evaluation, hciqc: HCI Quality Characteristic evaluates(hcie, hciqc) ∧ applies(hcie, hciec) ∧ usedToEvaluate(hciec, hciqc) ∧ refersTo(hciec, m) → quantifies(m, hciqc)
A Measure (e.g., time spent to log in the system) can be expressed in a Measure Unit (e.g., minute) and has a Scale partitioned according to the Measure Unit and composed of the values that can be associated to the Measure. Measurement consists in collecting Measured Values to a Measure (e.g., the measurement of the time to log in the system, resulting in the value 1 minute). In an HCI Evaluation, Measurements are performed to establish Measured Values to quantify HCI Quality Characteristics.
When a HCI Evaluation involves measurements, the HCI Evaluation Report must consider the Measured Values.
4. Concepts Definition
The following table shows the definitions for HCIEO concepts.
| Concept | Definition |
|---|---|
Person or Organization who participates in an HCI Evaluation by observing the human-computer interaction and collecting data for the evaluation. | |
Computer System that participates in an HCI Evaluation by collecting user interaction data (indirect observation), e.g., through interaction logs, for the evaluation. | |
Intentional event (i.e., a Complex Action) caused by the HCI Evaluator Intention and that consists in the systematic determination of the extent to which an Interactive Computer System (or its User Interface) quality characteristics meet the HCI Evaluation criteria considered in the evaluation. | |
Object intentionally made to specify evaluation criteria in the context of an evaluation. | |
Artifact Type required by HCI Evaluation Methods. | |
Conditions, or capacity needed (Requirement), used to evaluate interactive computer system’s quality characteristics. It can be determined by the HCI evaluation method of a certain HCI evaluation and may be related to user requirements. | |
A Procedure describing the actions to be performed by the HCI Evaluator to perform a HCI Evaluation. | |
Document that presents evaluation results and other relevant information such as the considered HCI Evaluation Criteria. | |
HCI Evaluator & Individual or organization (Stakeholder) that performs an HCI Evaluation. | |
The evaluation intended outcome. | |
Intention that inheres in a HCI Evaluator, causing him to perform an HCI Evaluation. | |
Role that can be played by an Agent (Agent HCI Observer) or a Computer System (Computer HCI Observer) who/which observes the human-computer interaction during an HCI Evaluation. | |
Characteristic expected in an Interactive Computer System (in software or hardware constituents), e.g., usability (software), screen size of a smart watch (hardware), among others. It can refer to the whole Interactive Computer System or part of it (e.g., its User Interface an Input Equipment). |
5. Detailed Concepts
Human-Computer Interaction Evaluation Ontology (HCIEO) detailed concepts.
HCIEO::Agent HCI Observer
Agent HCI Observer
Specializes:
UFO::Agent
HCIEO::HCI Observer
Definition:
Person or Organization who participates in an HCI Evaluation by observing the human-computer interaction and collecting data for the evaluation.
Example: during Usability Testing, a person (i.e., Agent HCI Observer) observes (direct observation) and collects user interaction data as the user interacts with the system.
Relations:
HCIEO::Computer HCI Observer
Computer HCI Observer
Specializes:
HCIO::Interactive Computer System
HCIEO::HCI Observer
Definition:
Computer System that participates in an HCI Evaluation by collecting user interaction data (indirect observation), e.g., through interaction logs, for the evaluation.
Example: a computer system automatically that collects interaction data during A/B Testing.
Relations:
HCIEO::HCI Evaluation
HCI Evaluation
Specializes:
UFO::Complex Action
Definition:
Intentional event (i.e., a Complex Action) caused by the HCI Evaluator Intention and that consists in the systematic determination of the extent to which an Interactive Computer System (or its User Interface) quality characteristics meet the HCI Evaluation criteria considered in the evaluation.
Example: evaluation of the usability of the checkout system of an e-commerce web site.
Source: adapted from (ISO/IEC 14598-5:1998; ISO/IEC 25066, 2016; ISO/TS 18152, 2010; ISO/IEC TR 25060, 2010; ISO/TR 16982, 2002; ISO 9241-220, 2019).
Relations:
HCI Evaluation (0..*) follows (1..*) HCI Evaluation Method
HCI Evaluation (1..1) creates (1..1) HCI Evaluation Report
HCI Evaluation (0..*) caused by (1..1) HCI Evaluator Intention
HCI Evaluation (0..*) evaluates (1..*) HCI Quality Characteristic
HCI Evaluation (0..*) evaluates (1..*) Interactive Computer System Participation
HCI Evaluation (1..1) uses (0..*) HCI Evaluation Artifact
HCI Evaluation (0..*) applies (1..*) HCI Evaluation Criteria
HCI Evaluation (0..*) evaluates (1..*) Human-Computer Interaction
HCI Evaluation (0..*) evaluates (1..1) Interactive Computer System
HCI Evaluation (0..*) evaluates (1..1) User Interface
User (0..*) participates in (0..*) HCI Evaluation
HCI Observer (1..*) participates in (1..*) HCI Evaluation
HCI Evaluator (1..*) performs (1..*) HCI Evaluation
HCIEO::HCI Evaluation Artifact
HCI Evaluation Artifact
Specializes:
SysSwO::Software Artifact
Definition:
Object intentionally made to specify evaluation criteria in the context of an evaluation.
Example: a checklist used during an evaluation to specify the criteria to be applied.
Relations:
HCI Evaluation Artifact (0..*) specifies (1..*) HCI Evaluation Criteria
HCI Evaluation Artifact (0..*) instance of (1..1) HCI Evaluation Artifact Type
HCI Evaluation (1..1) uses (0..*) HCI Evaluation Artifact
HCIEO::HCI Evaluation Artifact Type
HCI Evaluation Artifact Type
Specializes:
SysSwO::Software Artifact Type
Definition:
Artifact Type required by HCI Evaluation Methods.
Example: e.g., Checklist may be required by Usability Test.
Relations:
HCI Evaluation Method (0..*) requires the use of (0..*) HCI Evaluation Artifact Type
HCI Evaluation Artifact (0..*) instance of (1..1) HCI Evaluation Artifact Type
HCIEO::HCI Evaluation Criteria
HCI Evaluation Criteria
Specializes:
RSRO::Requirement
Definition:
Conditions, or capacity needed (Requirement), used to evaluate interactive computer system’s quality characteristics. It can be determined by the HCI evaluation method of a certain HCI evaluation and may be related to user requirements.
Example: total time the user spent on the first attempt to execute the task versus the time on the second attempt (the purpose of this data is to understand if the user can achieve a learning curve and on the second attempt to achieve the goal more quickly). In this case, the quality characteristic is usability, more specifically its learnability component.
Source: adapted from (ISO/IEC TR 25060, 2010; ISO 9241-220, 2019).
Relations:
HCI Evaluation Criteria (0..*) used to evaluate (1..*) HCI Quality Characteristic
HCI Evaluation Criteria specified according to HCI Evaluator Goal
HCI Evaluation Criteria (0..*) refers to (0..*) Measure
HCI Evaluation Criteria (0..*) refers to (0..*) User Requirement
HCI Evaluation Method (0..*) can determine (0..*) HCI Evaluation Criteria
HCI Evaluation (0..*) applies (1..*) HCI Evaluation Criteria
HCI Evaluation Artifact (0..*) specifies (1..*) HCI Evaluation Criteria
HCI Evaluation Report (0..*) reports (1..*) HCI Evaluation Criteria
HCI Evaluator Goal (0..*) helps to determine (1..*) HCI Evaluation Criteria
HCIEO::HCI Evaluation Method
HCI Evaluation Method
Specializes:
SPO::Method
Definition:
A Procedure describing the actions to be performed by the HCI Evaluator to perform a HCI Evaluation.
Example: heuristic evaluation, cognitive walkthroughs, standards inspection, pluralistic walkthroughs, usability test, consistency inspections, among others.
Source: adapted from (ISO/IEC 14598-5, 1998; ISO/TR 16982, 2002).
Relations:
HCI Evaluation Method (0..*) can determine (0..*) HCI Evaluation Criteria
HCI Evaluation Method (1..*) chosen according to (0..*) HCI Evaluator Goal
HCI Evaluation Method (0..*) requires the use of (0..*) HCI Evaluation Artifact Type
HCI Evaluation (0..*) follows (1..*) HCI Evaluation Method
HCI Evaluator Goal (1..1) helps to choose (1..*) HCI Evaluation Method
HCI Evaluator (1..*) choose (1..*) HCI Evaluation Method
HCIEO::HCI Evaluation Report
HCI Evaluation Report
Specializes:
SysSwO::Document
Definition:
Document that presents evaluation results and other relevant information such as the considered HCI Evaluation Criteria.
Example: Usability test report.
Source: adapted from (ISO/IEC 14598-5, 1998; ISO/IEC TR 25060, 2010).
Relations:
HCI Evaluation Report (0..*) reports (1..*) HCI Evaluation Criteria
HCI Evaluation Report (0..*) reports (0..*) Measured Value
HCI Evaluation (1..1) creates (1..1) HCI Evaluation Report
HCI Evaluator (1..*) responsible for (0..*) HCI Evaluation Report
HCIEO::HCI Evaluator
HCI Evaluator
Specializes:
SPO::Stakeholder
Definition:
HCI Evaluator & Individual or organization (Stakeholder) that performs an HCI Evaluation.
Example: usability specialists, developers.
Source: adapted from (ISO/TR 25060, 2010; ISO/IEC 25040, 2011).
Relations:
HCI Evaluator (1..*) performs (1..*) HCI Evaluation
HCI Evaluator (1..*) responsible for (0..*) HCI Evaluation Report
HCI Evaluator (1..*) choose (1..*) HCI Evaluation Method
HCI Evaluator Intention (1..*) inheres in (1..1) HCI Evaluator
HCIEO::HCI Evaluator Goal
HCI Evaluator Goal
Specializes:
UFO::Goal
Definition:
The evaluation intended outcome.
Example: Make the web site login UI more usable and understandable.
Relations:
HCI Evaluator Goal (1..1) propositional content of (1..*) HCI Evaluator Intention
HCI Evaluator Goal (0..*) helps to determine (1..*) HCI Evaluation Criteria
HCI Evaluator Goal (1..1) helps to choose (1..*) HCI Evaluation Method
HCI Evaluation Method (1..*) chosen according to (0..*) HCI Evaluator Goal
HCI Evaluation Criteria specified according to HCI Evaluator Goal
HCIEO::HCI Evaluator Intention
HCI Evaluator Intention
Specializes:
UFO::Intention
Definition:
Intention that inheres in a HCI Evaluator, causing him to perform an HCI Evaluation.
Example: the intention to evaluate an interactive computer system to find usability problems.
Relations:
HCI Evaluator Intention (1..*) inheres in (1..1) HCI Evaluator
HCI Evaluation (0..*) caused by (1..1) HCI Evaluator Intention
HCI Evaluator Goal (1..1) propositional content of (1..*) HCI Evaluator Intention
HCIEO::HCI Observer
HCI Observer
Specializes:
UFO::Rolemixin
Definition:
Role that can be played by an Agent (Agent HCI Observer) or a Computer System (Computer HCI Observer) who/which observes the human-computer interaction during an HCI Evaluation.
Relations:
HCI Observer (1..*) participates in (1..*) HCI Evaluation
HCIEO::HCI Quality Characteristic
HCI Quality Characteristic
Specializes:
UFO::Quality
UFO::Measurable Quality Universal
COM::Measurable Element
Definition:
Characteristic expected in an Interactive Computer System (in software or hardware constituents), e.g., usability (software), screen size of a smart watch (hardware), among others. It can refer to the whole Interactive Computer System or part of it (e.g., its User Interface an Input Equipment).
Example: usability of a smart watch, communicability of an UI login.
Source: adapted from (ISO 9241-11, 2018).
Relations:
HCI Quality Characteristic (1..*) inheres in (1..*) Human-Computer Interaction
Interactive Computer System (1..*) has (0..*) HCI Quality Characteristic
HCI Evaluation (0..*) evaluates (1..*) HCI Quality Characteristic
User Interface (1..*) has (0..*) HCI Quality Characteristic
HCI Evaluation Criteria (0..*) used to evaluate (1..*) HCI Quality Characteristic