The Human-Computer Interaction Ontology (HCIO)
core ontology from HCI-ON
HCIO published paperCosta, S. D., Barcellos, M. P., Falbo, R. de A., Conte, T., & de Oliveira, K. M. (2022). A core ontology on the Human–Computer Interaction phenomenon. Data & Knowledge Engineering, 138, 101977. 10.1016/j.datak.2021.101977
1. Ontology Description
The Human-Computer Interaction Ontology (HCIO), a reference ontology that aims to provide a common conceptualization of the Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) phenomenon and serves as a core ontology of HCI-ON. Given that a human-computer interaction involves communication between user and interactive computer system, HCIO is composed of sub-ontologies to deal with the interaction participants and with the interaction itself.
Given that a human-computer interaction involves communication between user and interactive computer system, HCIO is composed of sub-ontologies to deal with the interaction participants and with the interaction itself.
3. Ontology Models
Figure 1 presents the packages of the HCIO Modularization.
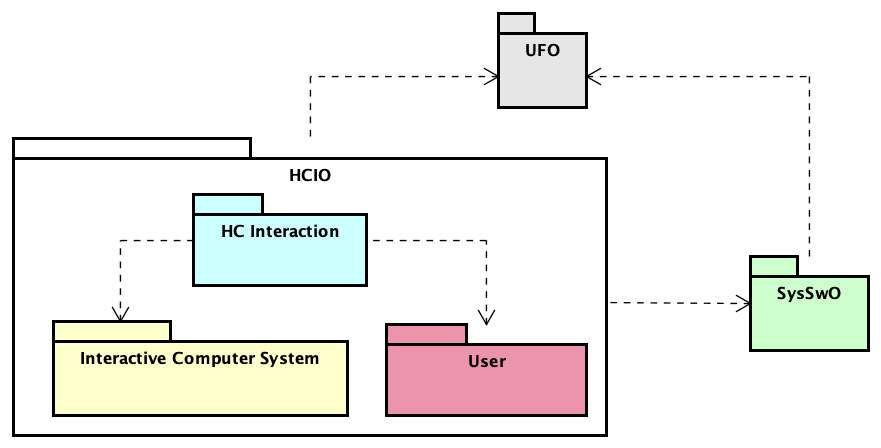
Figure 1. HCIO Modularization.
3.1. Interactive Computer System
Figure 2 presents the conceptual model of the Interactive Computer System subontology.
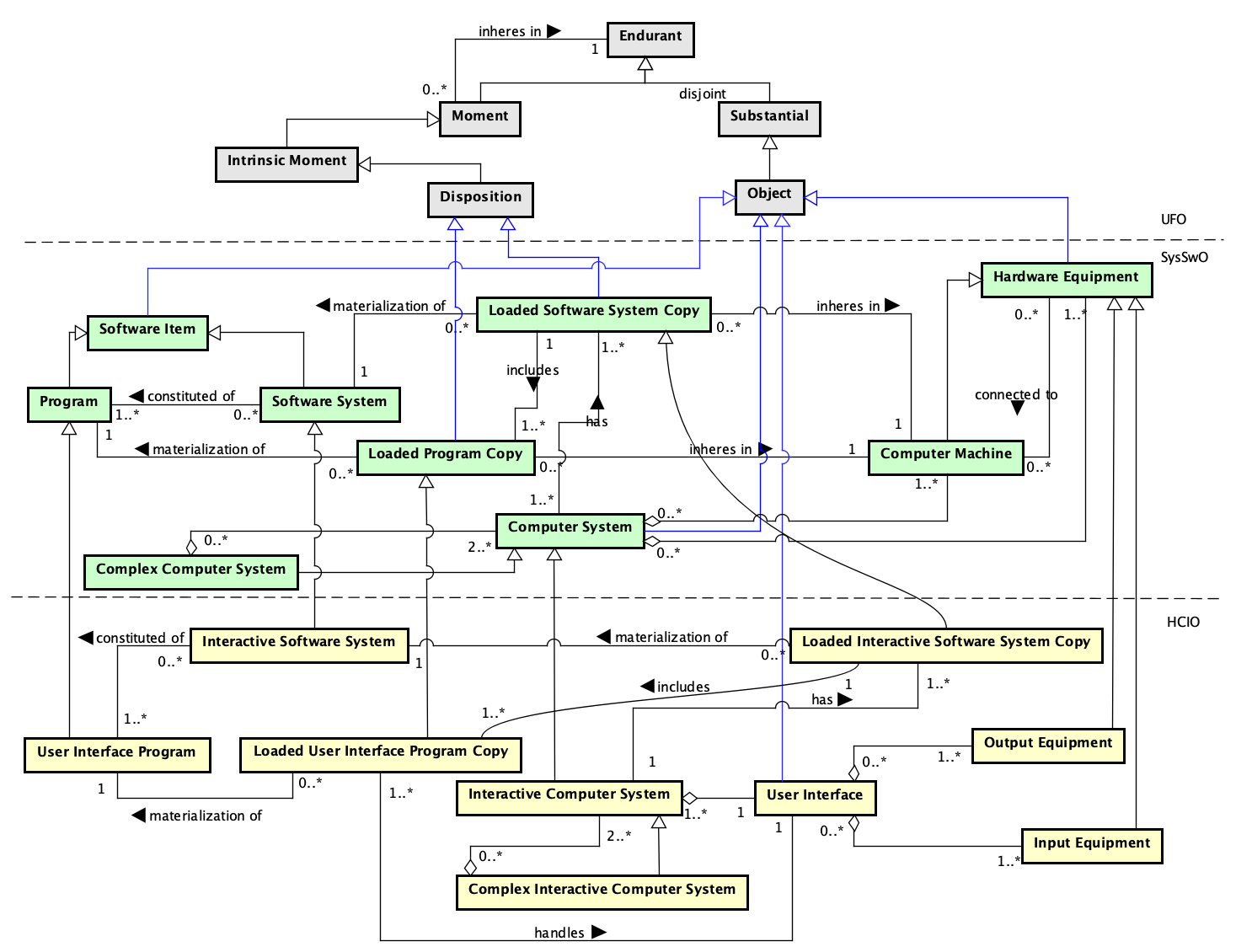
Figure 2. Interactive Computer System conceptual model.
The Interactive Computer System sub-ontology addresses what an interactive computer system is and its elements, including the user interface. It is mainly an extension of SysSwO (SEON Core Layer).
Interactive Computer System is a subtype of Computer System, and like the latter, it combines hardware and software. Concerning hardware, an Interactive Computer System is (the Computer System) composed of a set of Computer Machines and peripheral devices (Hardware Equipment) connected to them. The striking feature of an Interactive Computer System is that it has a User Interface, a complex Object that is composed of Input Equipment and Output Equipment connected to the Computer Machine. If an Output Equipment is part of a User Interface of an Interactive Computer System, then this Interactive Computer System should be constituted of the Computer Machine that connects the Output Equipment. The same applies to Input Equipment. These constraints are addressed by the following axioms:
A1. ∀ oeq: Output Equipment, ui: User Interface, ics: Interactive Computer System partOf(oeq, ui) ∧ partOf(ui, ics) → (∃ cm: Computer Machine partOf(cm, ics) ∧ connectedTo(oeq, cm))
A2. ∀ ieq: Input Equipment, ui: User Interface, ics: Interactive Computer System partOf(ieq, ui) ∧ partOf(ui, ics) → (∃ cm: Computer Machine partOf(cm, ics) ∧ connectedTo(ieq, cm))
When a Hardware Equipment is both an Input Equipment and an Output Equipment it is said an IO Equipment. Thus:
A3. ∀ he: Hardware Equipment Input Equipment(he) ∧ OutputEquipment(he) → IOEquipment(he)
Regarding software, an Interactive Computer System has a set of Software Systems (Interactive Software System) loaded in its Computer Machines (Loaded Interactive Software System Copies). The programs that constitute these systems are instances of Program. Some of them deal with aspects related to the user interface and, thus, are instances of User Interface Program. Thus, an Interactive Computer System has a User Interface and the copies of the programs loaded in its computer (Loaded User Interface Programs Copy) that handle its User Interface. The following axiom applies:
A4. ∀ ui: User Interface, ics: Interactive Computer System, lissc: Loaded Interactive Software System Copy partOf(ui, ics) ∧ has(ics, lissc) → ∃ luipc: Loaded User Interface Program Copy includes(lissc, luipc) ∧ handles(luipc, ui)
Interactive Computer Systems can form another Interactive Computer System, which is said a Complex Interactive Computer System.
3.2. User
Figure 3 presents the conceptual model of the User subontology.
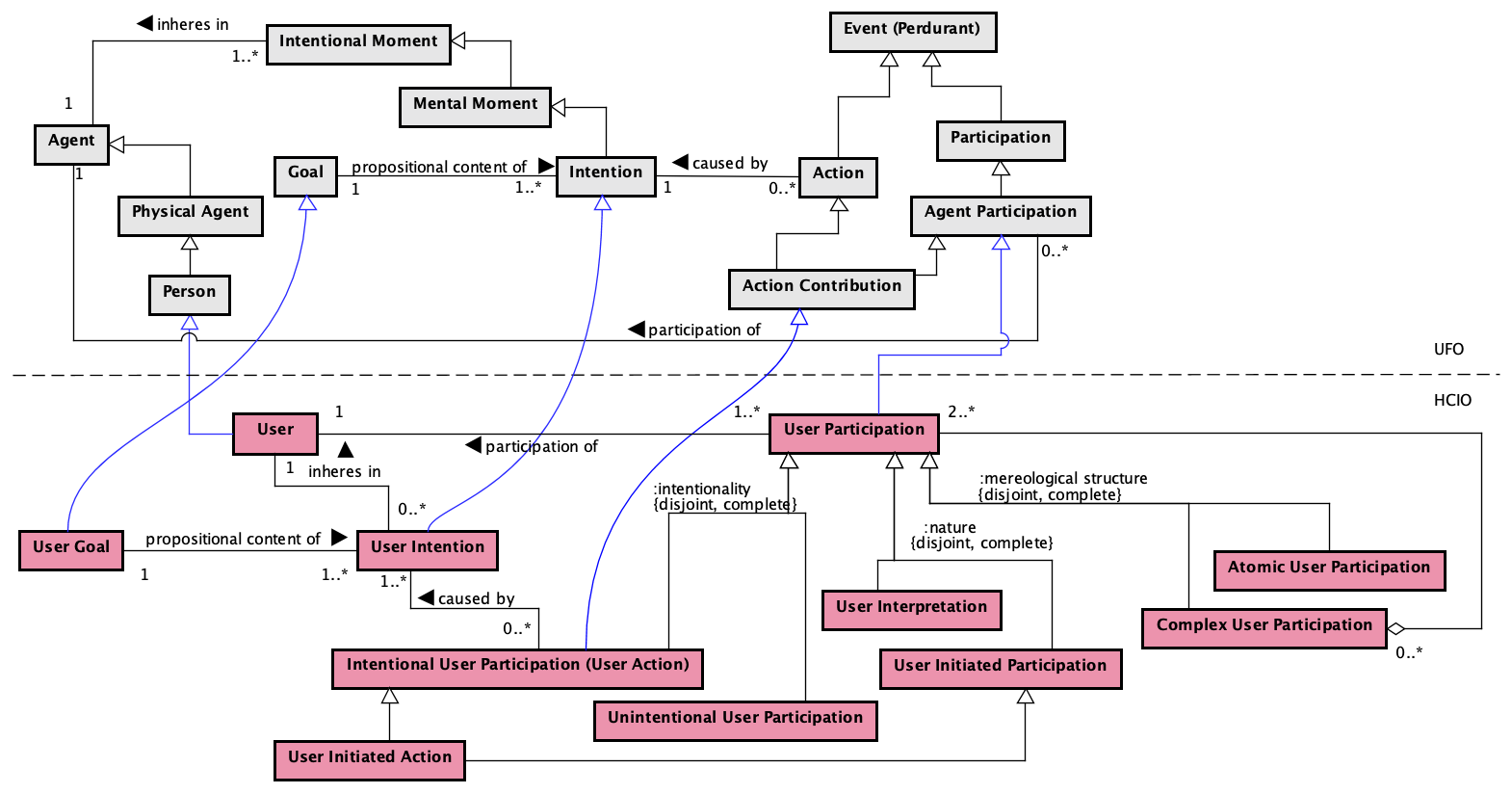
Figure 3. User conceptual model.
The User sub-ontology focuses on the user and its possible actions when interacting with an interactive computer system.
User is the role played by a Person that participates in a human-computer interaction. Such participation is said a User Participation, which can be either intentional (Intentional User Participation − or simply User Action) or unintentional (Unintentional User Participation).
In terms of UFO, User Participation is an Agent Participation. Intentional User Participation (User Action) is an Action Contribution, i.e., an intentional participation of a User. Intentional User Participations (User Actions) are caused by Intentions (User Intentions) that inhere in the User. As an Intention, User Intention has a Goal (more specifically a User Goal) as its propositional content. User Action, as an intentional participation, is performed by the User in order to achieve a User Goal. User Actions performed by a User can only be caused by User Intentions that inhere in that User. This constraint is addressed by the following axiom:
A5. ∀ user: User, ua: Intentional User Participation (User Action), uint: User Intention participationOf(ua, user) ∧ causedBy(ua, uint) → inheresIn(uint, user)
Considering its mereological structure, a User Participation can be an Atomic User Participation or a Complex User Participation, which is composed of others User Participations. In a Complex User Participation, all the User Participations are participations from the same User. Thus:
A6. ∀ cup: Complex User Participation, user: User, up: User Participation participationOf(cup, user) ∧ partOf(up, cup) → participationOf(up, user)
In another classification, which considers the nature of participations and is orthogonal to the ones discussed above, User Participations are classified into two disjoint types: User Initiated Participation and User Interpretation. User Initiated Participation refers to an act performed by the user making an input in the system. User Interpretation, in turn, regards interpreting a state of the system. When a User Initiated Participation is intentional, it is said a User Initiated Action.
3.3. HC Interaction
Figure 4 presents the conceptual model of the HC Interaction subontology.
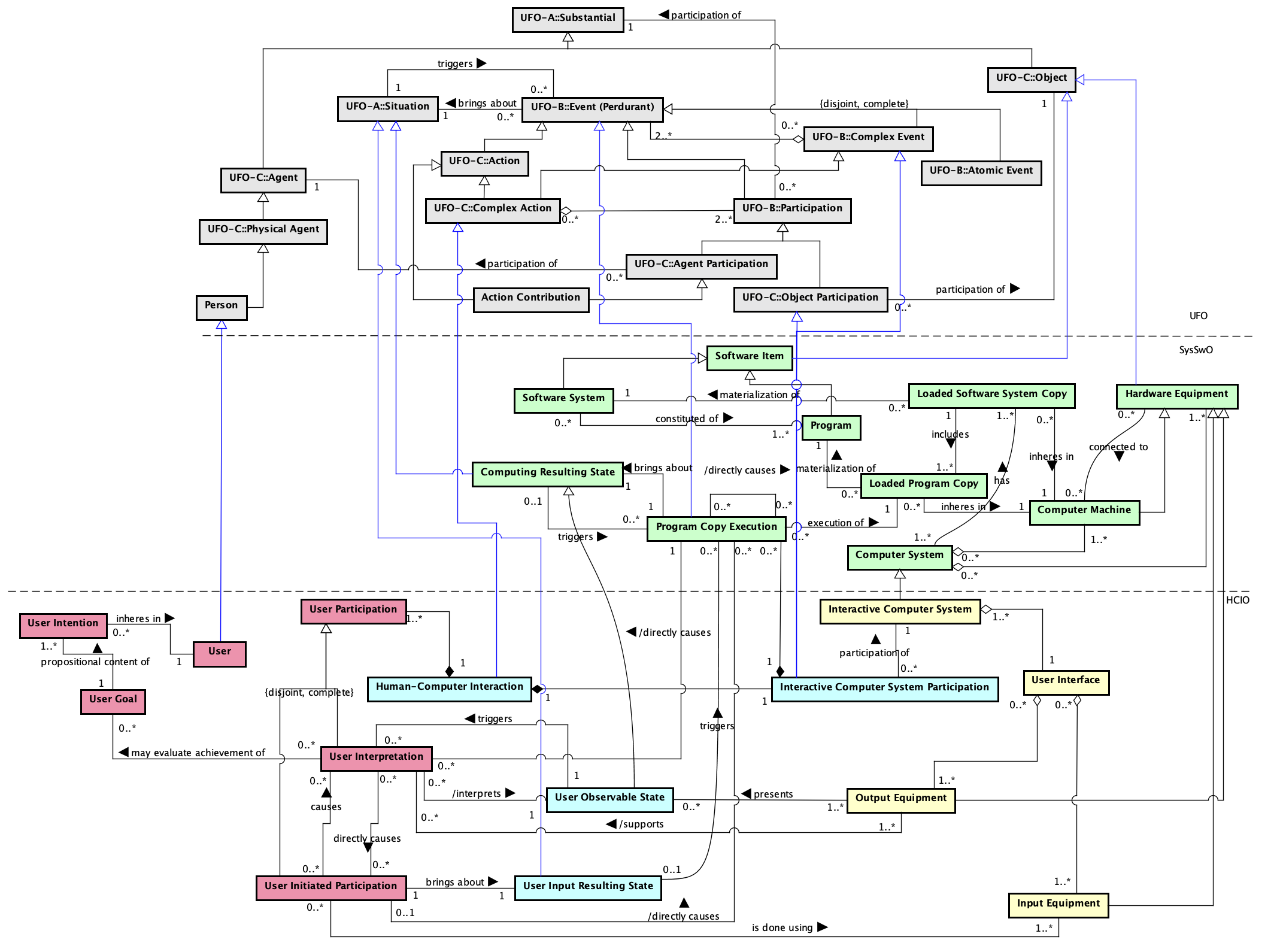
Figure 4. HC Interaction conceptual model.
The HC Interaction sub-ontology links concepts from the other two sub-ontologies to define what a human-computer interaction is.
A Human-Computer Interaction is an interaction between a User and an Interactive Computer System. Thus, a Human-Computer Interaction is composed by User Participations and an Interactive Computer System Participation (which can be composed of several Program Copy Executions), indicating the events performed by both parties in a specific interaction. It is important to notice that the events that compose a Human-Computer Interaction (i.e., the User Participation and the Program Copy Executions that compose the Interactive Computer System Participation) can have different granularities, depending on the needs of a particular domain.
As said before (see User Sub-ontology), in terms of UFO, User Participation is an Agent Participation. Interactive Computer System Participation, in turn, is an Object Participation. It is a Complex Event, since it aggregates all events performed by the Interactive Computer System in the context of a single Human-Computer Interaction. It is an Object Participation because, being the Interactive Computer System an Object, its participation is always unintentional.
A User Initiated Participation is performed using one or more Input Equipment. As a result of a User Initiated Participation, a User Input Resulting State is achieved. User Input Resulting State is a Situation representing the data entered by the user before any program execution. This situation triggers Program Copy Executions. Moreover, we can say that User Initiated Participation directly causes Program Copy Execution. Program Copy Execution brings about a Computing Resulting State (internal computer state), which, in turn, can trigger other Program Copy Executions. Thus, a Program Copy Execution can directly cause new Program Copy Executions.
Some Program Copy Executions can bring about a special type of Computing Resulting State, the one that is perceivable by user, said User Observable State. A User Observable State, thus, triggers User Interpretation. Therefore, we say that Program Copy Execution directly causes User Interpretation. In this context, the following axiom applies:
A7. ∀ ui: User Interpretation, uos: User Observable State, pce: Program Copy Execution, uirs: User Input Resulting State, uip: User Initiated Participation triggers(uos, ui) ∧ bringsAbout(pce, uos) ∧ triggers(uirs, pce) ∧ bringsAbout(uip, uirs) → causes(uip, ui)
It is important to say that (A7) does not constrain who are the users involved in the User Initiated Participation and in the User Interpretation, i.e., the User in the User Initiated Participation may be different from the one involved in the User Interpretation.
A User Observable State triggers User Interpretation and is presented by one or more Output Equipment. Thus, Output Equipment supports User Interpretation, i.e.:
A8. ∀ oe: Output Equipment, uos: User Observable State, ui: User Interpretation presents(oe, uos) ∧ triggers(uos, ui) → supports(oe, ui)
In a Human-Computer Interaction, both the Input and Output Equipment involved in the interaction should be part of the User Interface of the Interactive Computer System that participates in the interaction.
Since User Initiated Participation typically leads to some processing inside the system that results in an output to the user who can interpret it, we say that User Initiated Participation (indirectly) causes User Interpretation. User Interpretation may cause the User to act again. Thus, User Interpretation may directly cause (in terms of UFO) User Initiated Participations.
When a User Participation is intentional, it means that the User performed it considering some goal (User Goal). Interpretations performed by the user (User Interpretations) may evaluate User Goal achievement. This is a case of goal-driven behavior, in which a cycle of actions (User Participation) are repeated until the user achieves his/her goal (User Initiated Participation (indirectly) causes User Interpretation and User Interpretations (directly) causes User Initiated Participations).
The HC Interaction sub-ontology main purpose is to define what human-computer interaction is. In view of what was discussed, in summary, a Human-Computer Interaction is a Complex Event composed of User Participation and Interactive Computer System Participation. User Participation can involve both User Initiated Participations and User Interpretations. Interactive Computer System Participation regards the set of Program Executions performed by the Interactive Computer System in the interaction.
4. Concepts Definition
The following table shows the definitions for HCIO concepts.
| Concept | Definition |
|---|---|
Single User Participation. | |
Interactive Computer System composed of others Interactive Computer System | |
Participation composed of two or more User Participations. | |
An exchange of information (i.e., communication) between a User and an Interactive Computer System via the User Interface. | |
Hardware Equipment used to receive and transmit information or data from a User (input). | |
User participation intentionally performed. | |
Computer System that combines User Interface, Computer Machine and Loaded Software System Copies, used to process, transform, store, display or transmit information or data by receiving input, and communicating output to Users. | |
The participation of an Interactive Computer System in a Human-Computer Interaction. | |
Software system that includes, among other programs, User Interface Programs. | |
Loaded Software System Copy that is the materialization of an Interactive Software System. | |
Loaded Program Copy that is the materialization of a User Interface Program. | |
Hardware Equipment used to transmit or display information or data, communicating output to Users. | |
User participation unintentionally performed. | |
A Person who interacts with (or is expected to interact with) an Interactive Computer System. | |
The propositional content of something the User wants to achieve (User Intention). | |
Intentional User Action of inputting data or information using an Input Equipment. | |
Event in which a User inputs data or information using an Input Equipment. | |
A situation achieved as the result of User’s input (data or information) received by means of an Input Equipment. | |
An Intention that inheres in a User, causing him to perform intentional user actions. | |
All components of an interactive system (software or hardware) that provide information and controls for the user to accomplish specific tasks with the interactive system. | |
Program that deals with aspects related to the User Interface. | |
Event in which a User interprets the system output. | |
A situation (an Observable State) perceivable by Users, typically achieved as the result (output) of a Program Copy Execution, communicated or presented by an Output Equipment. | |
Event in which the user participates in a Human-Computer Interaction. |
5. Detailed Concepts
Human-Computer Interaction Ontology (HCIO) detailed concepts.
HCIO::Atomic User Participation
Atomic User Participation
Specializes:
HCIO::User Participation
Definition:
Single User Participation.
Example: user touching her finger to unlock her mobile phone by using her fingerprint; user clicking a button.
Relations:
HCIO::Complex Interactive Computer System
Complex Interactive Computer System
Specializes:
HCIO::Interactive Computer System
Definition:
Interactive Computer System composed of others Interactive Computer System
Example: IoT in a smart home.
Source: adapted from (ISO 9241-210, 2019) (ISO 9241-11, 2018).
Relations:
Complex Interactive Computer System (0..*) <>-- (2..*) Interactive Computer System
HCIO::Complex User Participation
Complex User Participation
Specializes:
HCIO::User Participation
Definition:
Participation composed of two or more User Participations.
Example: user typing her password and then answering security questions to log in the e-mail system.
Relations:
Complex User Participation (0..*) <>-- (2..*) User Participation
HCIO::Human-Computer Interaction
Human-Computer Interaction
Specializes:
UFO::Complex Action
COM::Measurable Entity
Definition:
An exchange of information (i.e., communication) between a User and an Interactive Computer System via the User Interface.
Example: user touching her finger to unlock her mobile phone by using her fingerprint and the mobile phone system showing a message informing that the fingerprint was not recognized; user entering a room, in a smart home, which automatically turns on the light.
Source: adapted from (ISO 9241-210, 2019).
Relations:
Human-Computer Interaction comunicates user input User Interface
Human-Computer Interaction (1..1) <>-- (1..1) Interactive Computer System Participation
Human-Computer Interaction <>-- (1..1) User Participation
HCI Quality Characteristic (1..*) inheres in (1..*) Human-Computer Interaction
HCI Evaluation (0..*) evaluates (1..*) Human-Computer Interaction
User Interface comunicates system output Human-Computer Interaction
HCIO::Input Equipment
Input Equipment
Specializes:
SysSwO::Hardware Equipment
Definition:
Hardware Equipment used to receive and transmit information or data from a User (input).
Example: keyboard, mouse, sensors.
Source: adapted from (Dix et al., 2004).
Relations:
Input Equipment (1..*) is done using (0..*) User Initiated Participation
Interactive Computer System (0..*) <>-- (1..*) Input Equipment
User Interface (0..*) <>-- (1..*) Input Equipment
HCIO::Intentional User Participation (User Action)
Intentional User Participation (User Action)
Specializes:
HCIO::User Participation
UFO::Action Contribution
Definition:
User participation intentionally performed.
Example: user touching her finger to unlock her mobile phone by using her fingerprint; user clicking the send button to send an e-mail.
Relations:
Intentional User Participation (User Action) (0..*) caused by (1..*) User Intention
HCIO::Interactive Computer System
Interactive Computer System
Specializes:
SysSwO::Hardware Equipment
SysSwO::Computer System
COM::Measurable Entity
Definition:
Computer System that combines User Interface, Computer Machine and Loaded Software System Copies, used to process, transform, store, display or transmit information or data by receiving input, and communicating output to Users.
Example: a desktop computer, its monitor, keyboard, mouse and software systems loaded in the computer (operational system, browser, text editor, etc.); smart watch; smart mobile phone.
Source: adapted from (ISO 9241-210, 2019).
Relations:
Interactive Computer System <>-- User Interface
Interactive Computer System <>-- Hardware Equipment
Interactive Computer System (0..*) <>-- (1..*) Input Equipment
Interactive Computer System <>-- User Input Resulting State
Interactive Computer System (1..1) has (1..*) Loaded Interactive Software System Copy
Interactive Computer System (1..*) has (0..*) HCI Quality Characteristic
Complex Interactive Computer System (0..*) <>-- (2..*) Interactive Computer System
HCI Evaluation (0..*) evaluates (1..1) Interactive Computer System
Interactive Computer System Participation (0..*) participation of (1..1) Interactive Computer System
HCIO::Interactive Computer System Participation
Interactive Computer System Participation
Specializes:
UFO::Object Participation
UFO::Complex Event
Definition:
The participation of an Interactive Computer System in a Human-Computer Interaction.
Example: the participation of the mobile phone system in the human-computer interaction in which the user touches her finger to unlock her mobile phone by using her fingerprint and the mobile phone system shows a message informing that the fingerprint was not recognized; the participation of the smart watch in the human-computer interaction in which the user uses the smart watch to monitor her heart pulse.
Relations:
Interactive Computer System Participation (0..*) participation of (1..1) Interactive Computer System
Interactive Computer System Participation (1..1) <>-- (0..*) Program Copy Execution
HCI Evaluation (0..*) evaluates (1..*) Interactive Computer System Participation
Human-Computer Interaction (1..1) <>-- (1..1) Interactive Computer System Participation
HCIO::Interactive Software System
Interactive Software System
Specializes:
SysSwO::Software System
Definition:
Software system that includes, among other programs, User Interface Programs.
Example: a home banking system and its graphical programs that deals with user interface aspects.
Relations:
Interactive Software System (0..*) constituted of (1..*) User Interface Program
Loaded Interactive Software System Copy (0..*) materialization of (1..1) Interactive Software System
HCIO::Loaded Interactive Software System Copy
Loaded Interactive Software System Copy
Specializes:
SysSwO::Loaded Software System Copy
Definition:
Loaded Software System Copy that is the materialization of an Interactive Software System.
Example: the copy of the home banking system loaded in the computer of a certain user.
Relations:
Loaded Interactive Software System Copy (0..*) materialization of (1..1) Interactive Software System
Loaded Interactive Software System Copy (1..1) includes (1..*) Loaded User Interface Program Copy
Interactive Computer System (1..1) has (1..*) Loaded Interactive Software System Copy
HCIO::Loaded User Interface Program Copy
Loaded User Interface Program Copy
Specializes:
SysSwO::Loaded Program Copy
Definition:
Loaded Program Copy that is the materialization of a User Interface Program.
Example: the copy of the programs that deal with interface aspects of the home banking system loaded in the computer of a certain user.
Relations:
Loaded User Interface Program Copy (0..*) materialization of (1..1) User Interface Program
Loaded User Interface Program Copy (1..*) handles (1..1) User Interface
User Interface (1..1) handles (1..*) Loaded User Interface Program Copy
Loaded Interactive Software System Copy (1..1) includes (1..*) Loaded User Interface Program Copy
HCIO::Output Equipment
Output Equipment
Specializes:
SysSwO::Hardware Equipment
Definition:
Hardware Equipment used to transmit or display information or data, communicating output to Users.
Example: Monitor, speaker, etc.
Source: adapted from (Dix et al., 2004).
Relations:
Output Equipment (1..*) presents (0..*) User Observable State
Output Equipment (1..*) /supports (0..*) User Interpretation
User Interface (0..*) <>-- (1..*) Output Equipment
HCIO::Unintentional User Participation
Unintentional User Participation
Specializes:
HCIO::User Participation
Definition:
User participation unintentionally performed.
Example: a user walking and unintentionally giving information about number of steps to a monitoring system loaded in her smart watch; user entering a room, in a smart home, which automatically turns on the light.
Relations:
HCIO::User
User
Specializes:
UFO::Person
Definition:
A Person who interacts with (or is expected to interact with) an Interactive Computer System.
Example: a person who uses a home banking system, smart watch or smart mobile phone.
Source: adapted from (ISO 9241-210, 2019).
Relations:
User (0..*) participates in (0..*) HCI Evaluation
User Participation (1..*) participation of (1..1) User
User Intention (0..*) inheres in (1..1) User
HCIO::User Goal
User Goal
Specializes:
UFO::Goal
Definition:
The propositional content of something the User wants to achieve (User Intention).
Example: the goal of buying fly tickets to go on vacation.
Relations:
User Goal (1..1) propositional content of (1..*) User Intention
User Interpretation (0..*) may evaluate achievement of (0..*) User Goal
User Requirement (0..*) refers to (1..*) User Goal
HCIO::User Initiated Action
User Initiated Action
Specializes:
HCIO::User Initiated Participation
HCIO::Intentional User Participation (User Action)
Definition:
Intentional User Action of inputting data or information using an Input Equipment.
Example: user touching her finger to unlock her mobile phone by using her fingerprint; user clicking the send button to send an email.
Relations:
HCIO::User Initiated Participation
User Initiated Participation
Specializes:
HCIO::User Participation
Definition:
Event in which a User inputs data or information using an Input Equipment.
Example: user touching her finger to unlock her mobile phone by using her fingerprint.
Relations:
User Initiated Participation (0..*) causes (0..*) User Interpretation
User Initiated Participation (1..1) brings about (1..1) User Input Resulting State
User Initiated Participation (0..1) /directly causes (0..*) Program Copy Execution
User Interpretation (0..*) directly causes (0..*) User Initiated Participation
Input Equipment (1..*) is done using (0..*) User Initiated Participation
HCIO::User Input Resulting State
User Input Resulting State
Specializes:
UFO::Situation
Definition:
A situation achieved as the result of User’s input (data or information) received by means of an Input Equipment.
Example: the user fingerprint captured by the mobile phone system; the button clicked.
Relations:
User Input Resulting State (0..1) triggers (0..*) Program Copy Execution
User Input Resulting State (0..*) satisfies (0..*) Mental User Input Resulting State
Interactive Computer System <>-- User Input Resulting State
User Initiated Participation (1..1) brings about (1..1) User Input Resulting State
HCIO::User Intention
User Intention
Specializes:
UFO::Intention
Definition:
An Intention that inheres in a User, causing him to perform intentional user actions.
Example: the intention to travel on vacation.
Relations:
User Intention (0..*) inheres in (1..1) User
User Goal (1..1) propositional content of (1..*) User Intention
Intentional User Participation (User Action) (0..*) caused by (1..*) User Intention
HCIO::User Interface
User Interface
Specializes:
UFO::Object
COM::Measurable Entity
Definition:
All components of an interactive system (software or hardware) that provide information and controls for the user to accomplish specific tasks with the interactive system.
Example: mouse, keyboard, monitor, sensors and the software that handle them.
Source: adapted from (ISO 9241-210, 2019; ISO 9241-112, 2017).
Relations:
User Interface <>-- Software Product
User Interface <>-- Hardware Equipment
User Interface comunicates system output Human-Computer Interaction
User Interface shows Computing Resulting State
User Interface (0..*) <>-- (1..*) Input Equipment
User Interface (0..*) <>-- (1..*) Output Equipment
User Interface (1..1) handles (1..*) Loaded User Interface Program Copy
User Interface (1..*) has (0..*) HCI Quality Characteristic
Interactive Computer System <>-- User Interface
HCI Evaluation (0..*) evaluates (1..1) User Interface
Human-Computer Interaction comunicates user input User Interface
Loaded Program Copy (1..*) handles (0..1) User Interface
Loaded User Interface Program Copy (1..*) handles (1..1) User Interface
HCIO::User Interface Program
User Interface Program
Specializes:
SysSwO::Program
Definition:
Program that deals with aspects related to the User Interface.
Example: the program responsible for the graphical user interface of the component that captures the user fingerprint to unlock a mobile phone.
Relations:
User Interface Program (0..*) implements (1..*) Quality Characteristic
Interactive Software System (0..*) constituted of (1..*) User Interface Program
Loaded User Interface Program Copy (0..*) materialization of (1..1) User Interface Program
HCIO::User Interpretation
User Interpretation
Specializes:
HCIO::User Participation
Definition:
Event in which a User interprets the system output.
Example: user interpreting a message from the mobile phone system informing that the captured fingerprint was not recognized; user sensing her smart watch vibrate; user hearing the notification sound of new message.
Relations:
User Interpretation (0..*) directly causes (0..*) User Initiated Participation
User Interpretation (0..*) may evaluate achievement of (0..*) User Goal
User Interpretation (0..*) interprets (1..1) User Observable State
User Interpretation (0..*) /interprets (1..1) User Observable State
Output Equipment (1..*) /supports (0..*) User Interpretation
Program Copy Execution (1..1) /directly causes (0..*) User Interpretation
User Observable State (1..1) triggers (0..*) User Interpretation
User Initiated Participation (0..*) causes (0..*) User Interpretation
HCIO::User Observable State
User Observable State
Specializes:
SysSwO::Computing Resulting State
Definition:
A situation (an Observable State) perceivable by Users, typically achieved as the result (output) of a Program Copy Execution, communicated or presented by an Output Equipment.
Example: a message shown in the mobile phone screen informing the user that the captured fingerprint was not recognized, smart watch vibrating; sounds emitted by the mobile phone.
Relations:
User Observable State (1..1) triggers (0..*) User Interpretation
User Observable State (0..*) satisfies (0..*) Mental User Observable State
Output Equipment (1..*) presents (0..*) User Observable State
User Interpretation (0..*) interprets (1..1) User Observable State
User Interpretation (0..*) /interprets (1..1) User Observable State
HCIO::User Participation
User Participation
Specializes:
UFO::Agent Participation
COM::Measurable Entity
Definition:
Event in which the user participates in a Human-Computer Interaction.
Example: user walking and unintentionally giving information about number of steps to a monitoring system loaded in her smart watch; user touching her finger to unlock her mobile phone by using her fingerprint; user interpreting a message from the mobile phone system informing that the captured fingerprint was not recognized.
Relations:
User Participation (1..*) participation of (1..1) User
Human-Computer Interaction <>-- (1..1) User Participation
Complex User Participation (0..*) <>-- (2..*) User Participation
References
-
Dix, A., Finlay, J. E., Abowd, G. D., & Beale, R. (2004). Human-Computer Interaction (3rd ed., p. 834). Pearson Prentice-Hall, Inc. [bibtex]